Utilities Overview for AhsayOBM
Utilities Overview
This allows the user to perform quality check on the backed up data, free up storage from obsolete files, delete, and decrypt backed up data.
There are four (4) functions available for this feature, namely:
Data Integrity Check
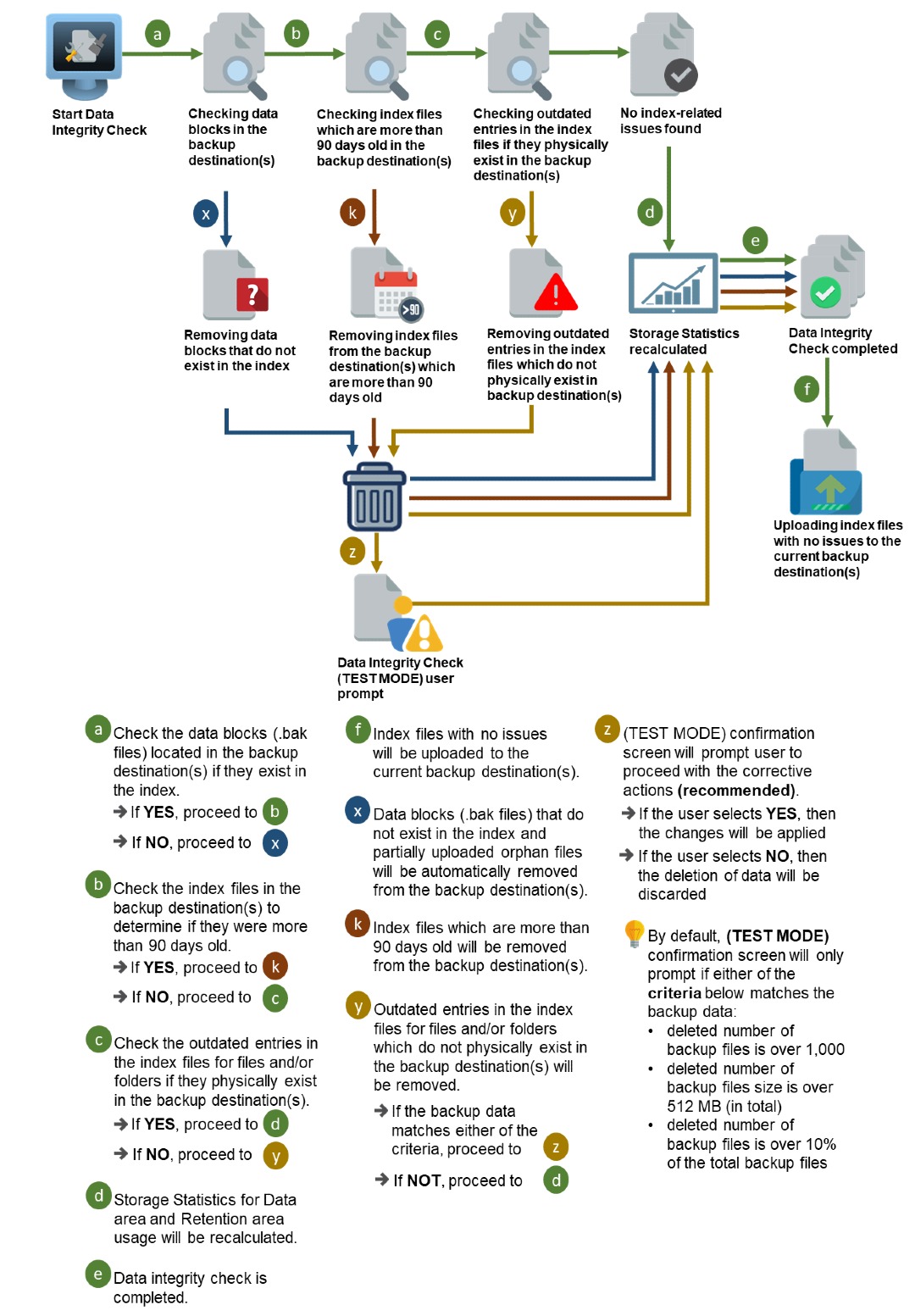
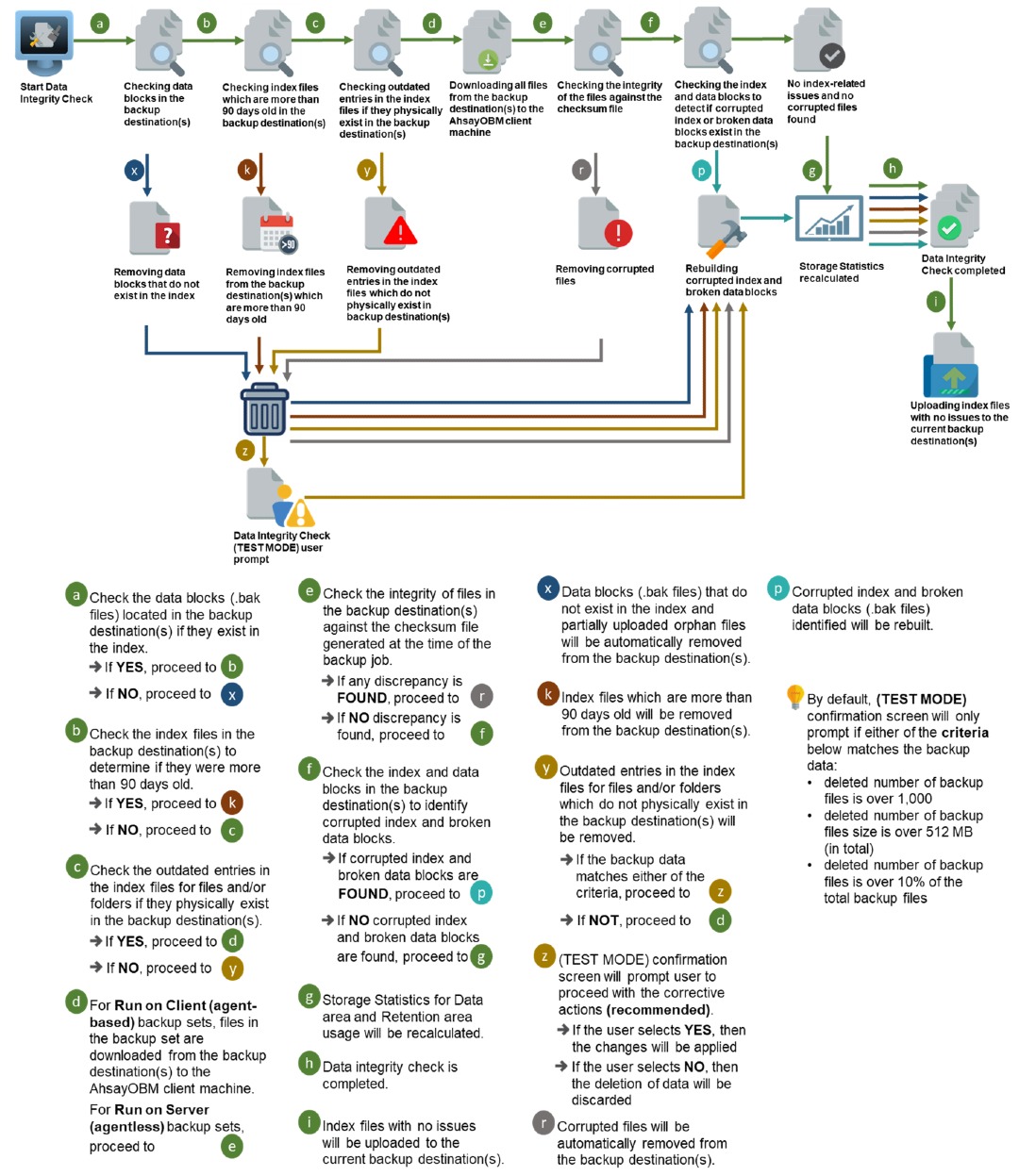
The Data Integrity Check (DIC) is used to identify the data in the backup set that has index-related issues, remove any corrupted file(s) from the backup destination(s) to ensure the integrity of the backup data and its restorability, and update the storage statistics.
For an efficient management of overall storage size of the backup destination(s), the data integrity check job will perform check for the backup destination(s) to remove old index files that are more than ninety (90) days old in the backup job folder(s).
- Data Integrity Check CANNOT fix or repair files that are already corrupted.
- Data Integrity Check can only be started if there is NO active backup or restore job(s) running on the backup set selected for the DIC job. As the backup, restore and data integrity check are using the same index for read and write operations. Otherwise, an error message will be displayed in the post-DIC to indicate that the data integrity check is completed with error(s) and had skipped a backup set with an active backup job.
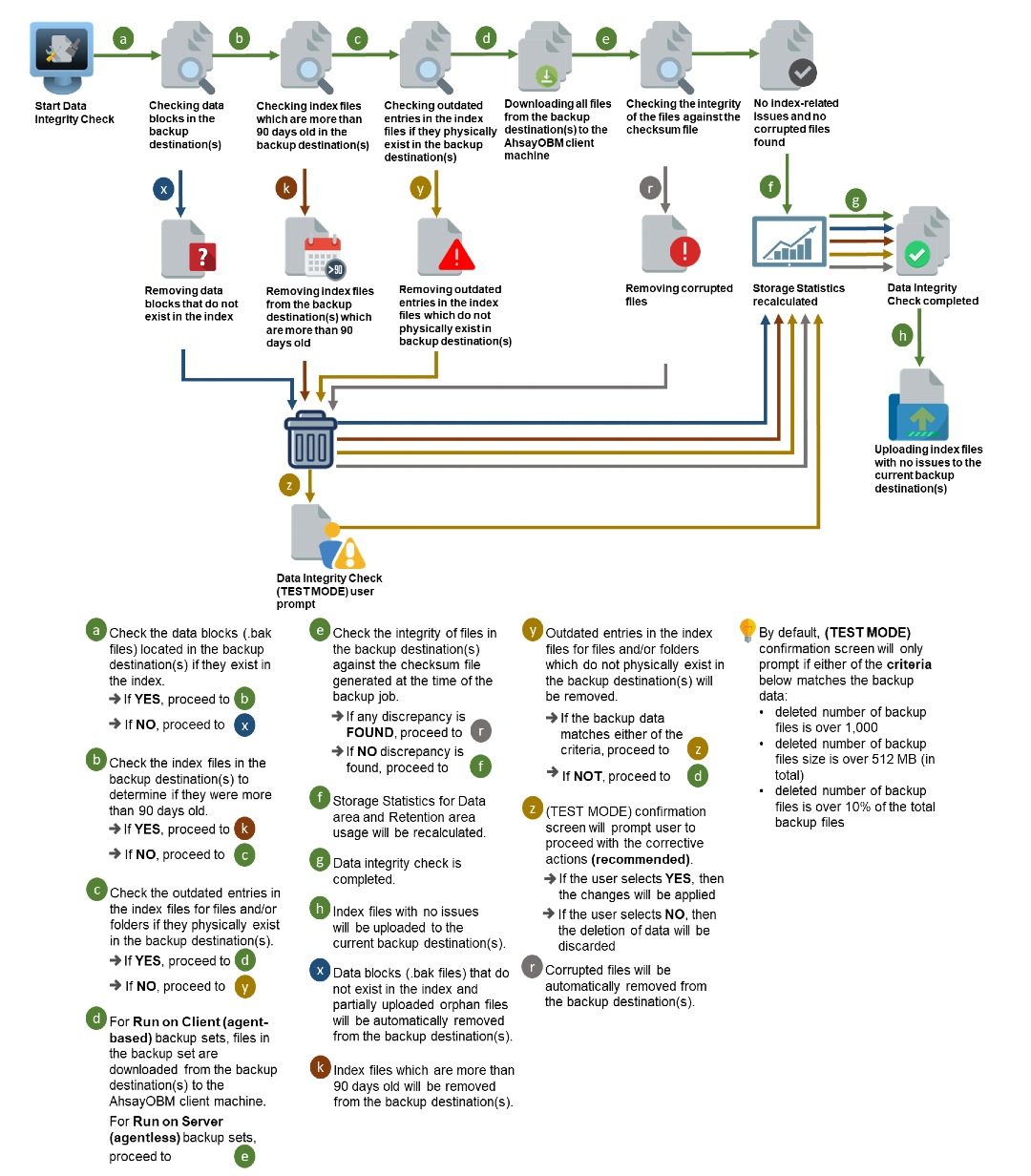
Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
When this option is enabled, the DIC will perform check on the integrity of the files on the backup destination(s) against the checksum file generated at the time of the backup job.
If there is a discrepancy, this indicates that the files on the backup destination(s) are corrupted and will be removed from the backup destination(s). If these files still exist on the client machine on the next backup job, AhsayOBM will upload the latest copy of the files.
However, if the corrupted files are in the Retention Area, they will not be backed up again as the source file has already been deleted from the client machine.
The time required to complete a data integrity check depends on several factors such as:
- number of files and/or folders in the backup set(s)
- bandwidth available on the client computer
- hardware specifications of the client computer such as, the disk I/O and CPU performance
- For user(s) with metered internet connection, additional data charges may be incurred if the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) is enabled. As CRC data involves downloading the data from the backup destination(s) to the client machine in order to perform this check.
- To find out how much data is downloaded from the backup destination(s) for the CRC check, please refer to the value for Utilities in the Data Transfer statistics section.
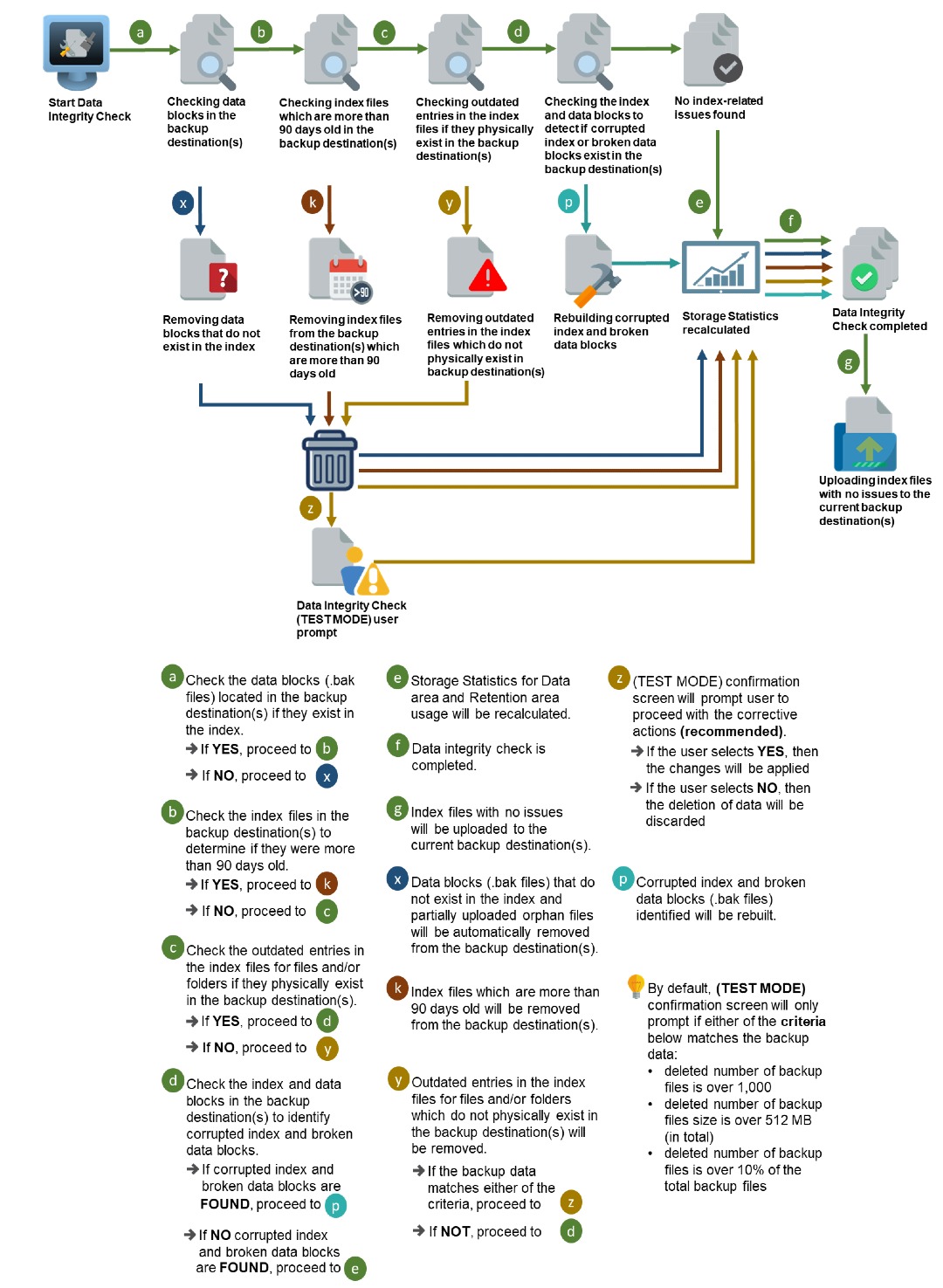
Rebuild Index
When this option is enabled, the DIC will start rebuilding corrupted index and/or broken data blocks if there are any.
Empty All Files in Recycle Bin
When this option is enabled, all the files in the Recycle Bin will be deleted.
There are four (4) options in performing the Data Integrity Check:
| Settings | Function |
|---|---|
Option 1 | For checking of index and data. |
Option 2 | For checking of index and integrity of files against the checksum file generated at the time of the backup job. |
Option 3 | For checking and rebuilding of index. |
Option 4 | For checking of index, integrity of files against the checksum file generated at the time of the backup job and rebuilding of index. |
The following diagrams show the detailed process of the Data Integrity Check (DIC) in four (4) modes:
Option 1
Disabled Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Rebuild index - (Default mode)
Option 2
Enabled Run Cyclic Redundancy check (CRC) and Disabled Rebuild index.
Option 3
Disabled Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Enabled Rebuild index
Option 4
Enabled Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Rebuild index.
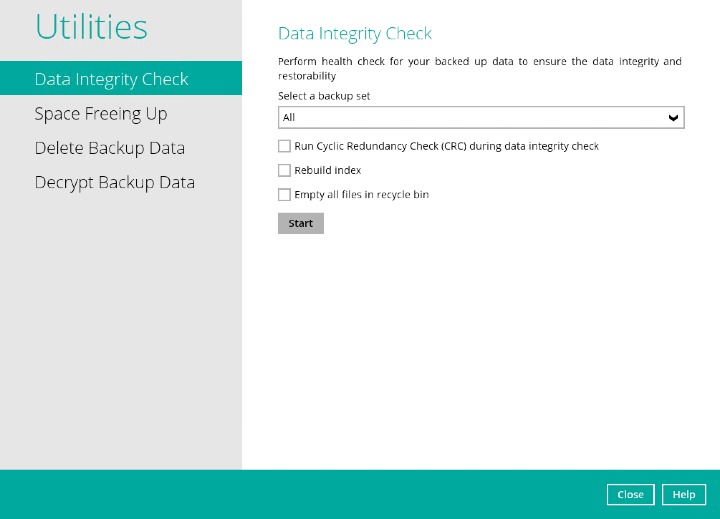
Perform Data Integrity Check
Go to the Data Integrity Check tab in the "Utilities" menu.
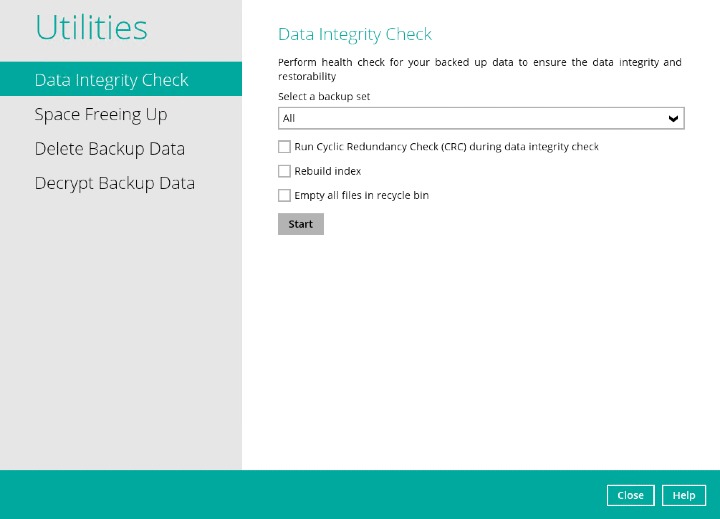
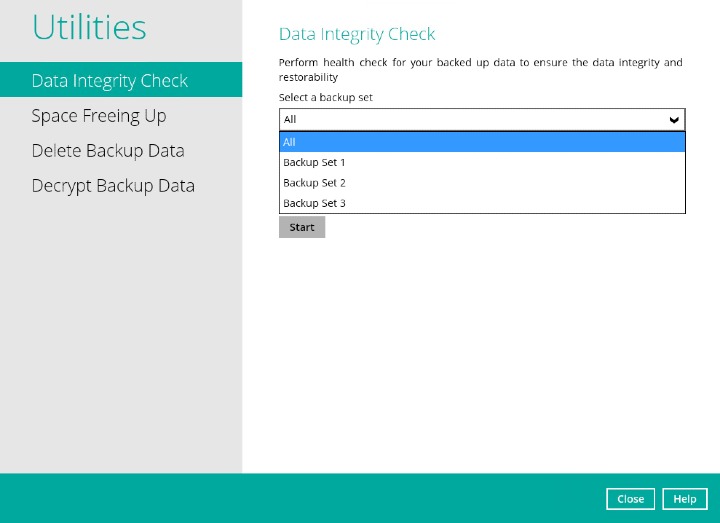
Click the drop-down button to select a backup set.
Click the drop-down button to select a backup destination.
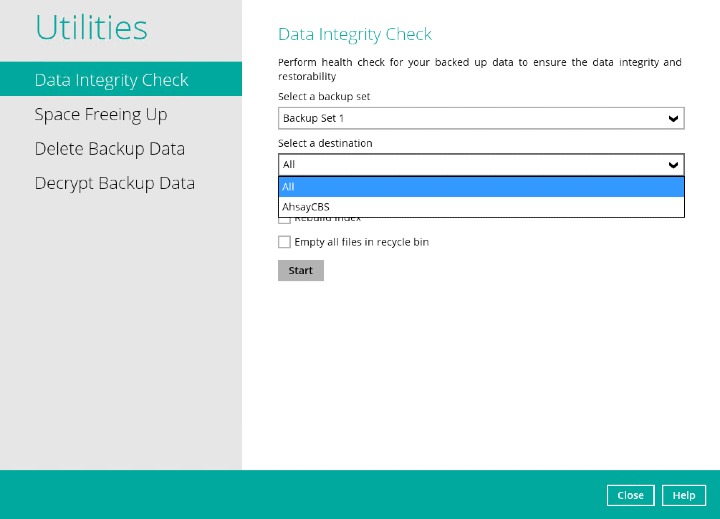
- Click the Start button to begin the Data Integrity Check
Provide the passcode for 2FA
 The passcode will only be required if the backup user account is setup with 2FA. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
The passcode will only be required if the backup user account is setup with 2FA. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.The Data Integrity Check will start running on the selected backup set(s) and backup destination(s).
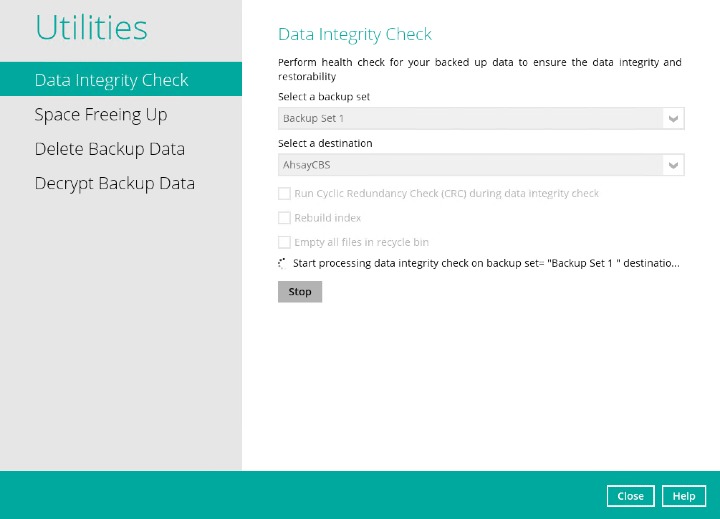
Once the Data Integrity Check job is completed, click the View log button to check the detailed DIC log.
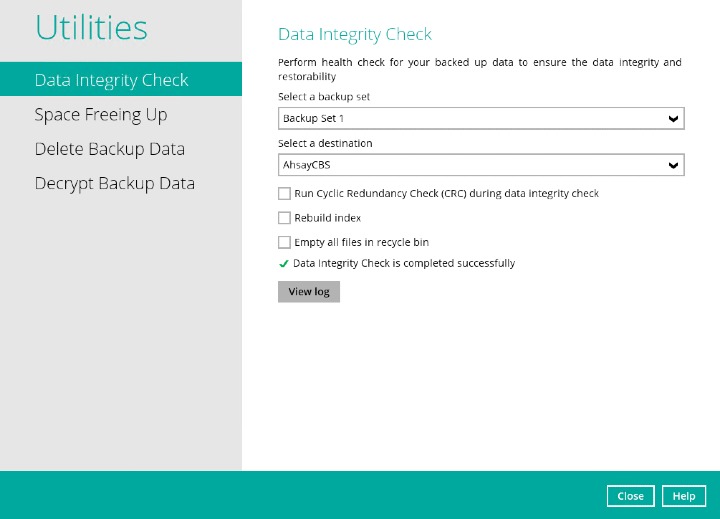
The detailed log of Data Integrity Check process will be displayed.
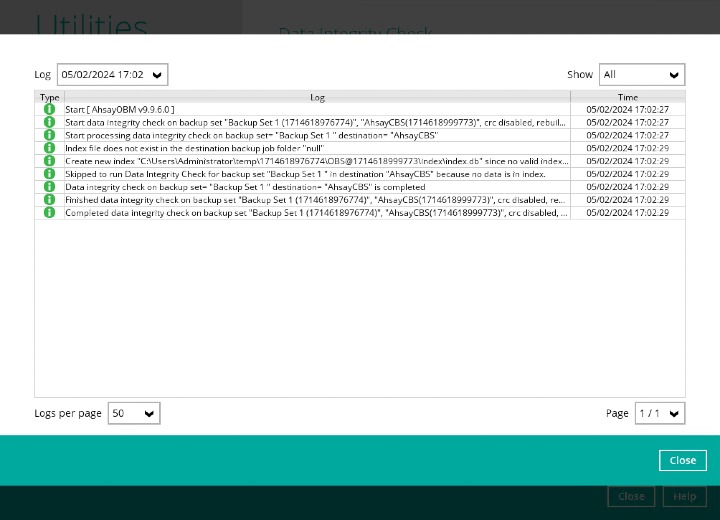
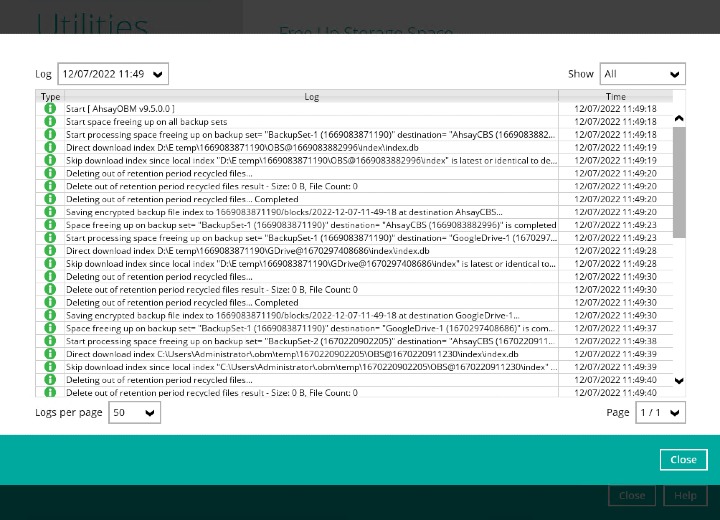
The following options can be used for further viewing of the detailed DIC log:
- Log filter
- Show filter
- Logs per page
- Page
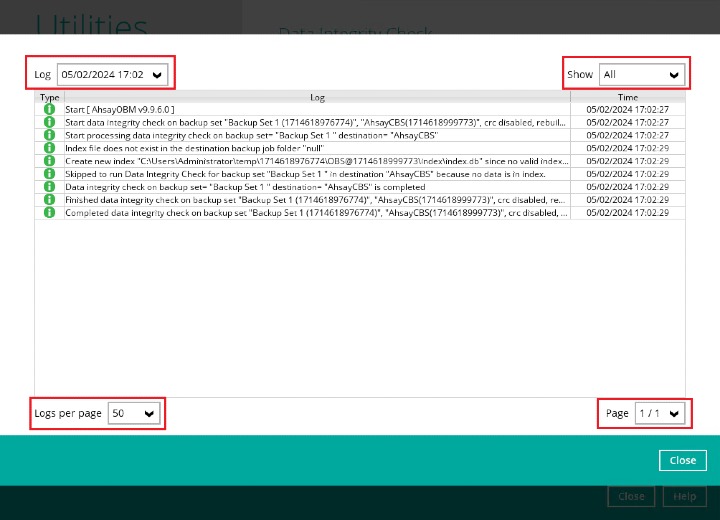
Settings Screenshot Function Log filter This option is used to display the available logs of the Data Integrity Check jobs. Show filter This option is used to sort the Data Integiry Check log by its status (i.e., All Information, Warning, and Error). Logs per page This option allows user to choose the displayed number of logs per page. Page This option allows user to navigate the logs to the next page(s). If the backup destination used for storing the backup set is an immutable destination, then the backup user account must be setup with 2FA in order to delete corrupted data blocks. If the backup user account does not have 2FA, DIC will proceed but there will be a warning in the logs since deleting of corrupted data blocks will not be allowed.
- Data Integrity Check is completed successfully with no data corruption or index-related issues detected.
- Corrupted data (e.g., index files, checksum files and/or broken data blocks) has been detected.
- Backup set that contains an error
- Backup Destination
- Items found in index
- Data corrupted items
- Index broken data blocks
- Statistics (i.e. Correct or Incorrect)
- deleted number of backup files is over 1,000
- deleted number of backup file size is over 512 MB (in total)
- deleted number of backup files is over 10% of the total backup files
on Windows, it is in:
%UserProfile%\.obm\system\IntegrityCheckon Linux GUI it is in:
$UserProfile/.obm/system/IntegrityCheckon Mac it is in:
$UserProfile/.obm/system/IntegrityCheck
Space Freeing Up
This feature is used to remove obsolete file(s) from your backup set and destination (manually start Retention Policy). After the Space Freeing Up job is completed, the storage statistics of the backup set(s) are updated.
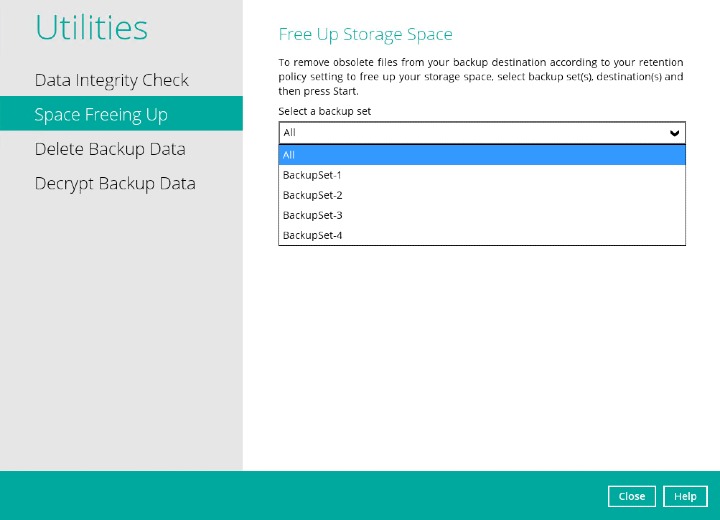
Select a backup set from the drop-down list
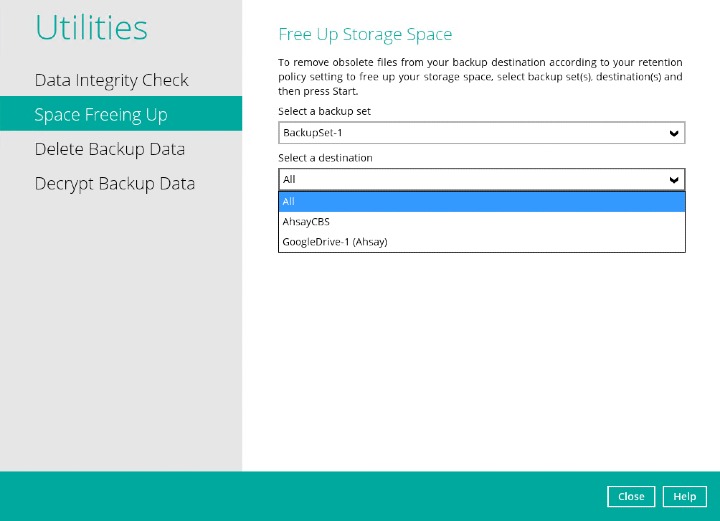
If you select a specific backup set, then you will also have to select a specific destination or all destinations.
If you select All backup sets, then there is no need to select a destination.
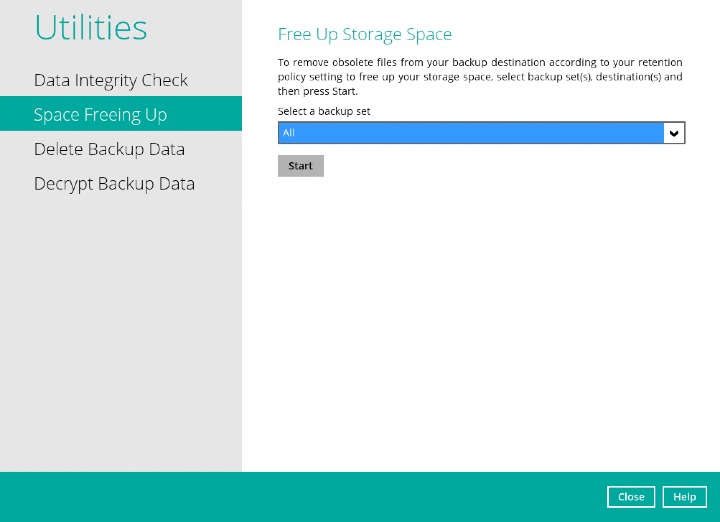
Click the Start button to perform a space free up.
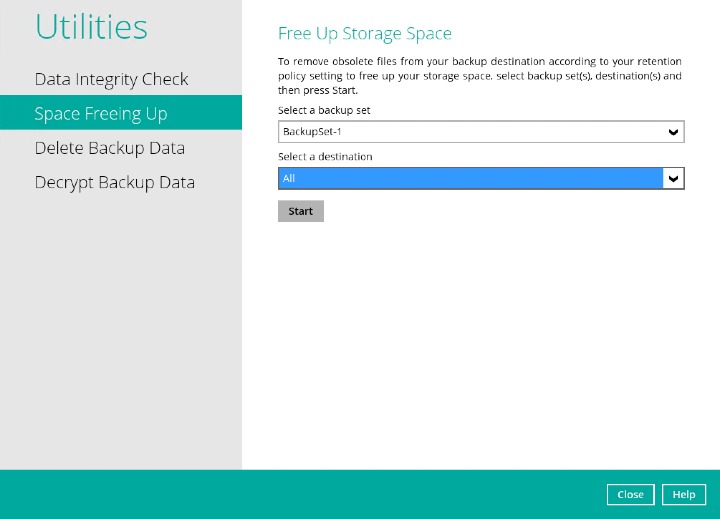
Provide the passcode for 2FA.

If the backup destination is immutable, space freeing up will not be allowed and this message will be displayed:
However, if deletion is enabled temporarily for the immutable backup destination, space freeing up will run after the passcode for 2FA is provided.
- The backup user account must be setup with 2FA in order to perform space free up from immutable backup destination.
- The passcode will only be required if 2FA is enabled for the user whether the backup destination is immutable or not. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
Space freeing job will start running on the selected backup set(s) and backup destination(s).
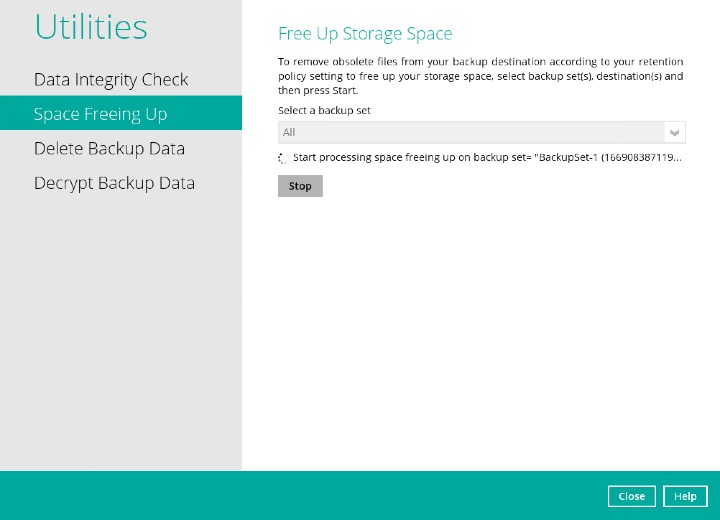
The status will be shown once completed.
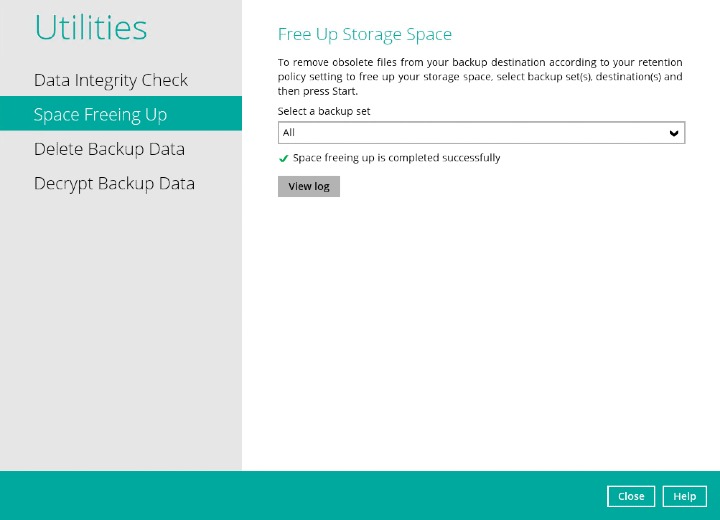
Click the View log button to see the detailed report of the space freeing up job.
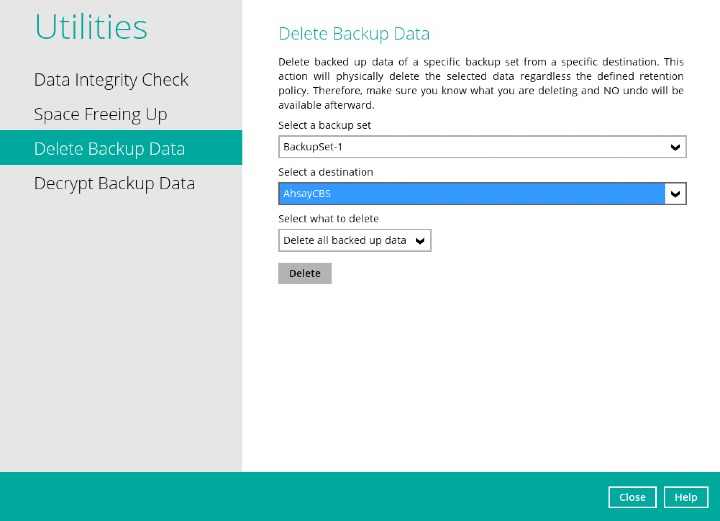
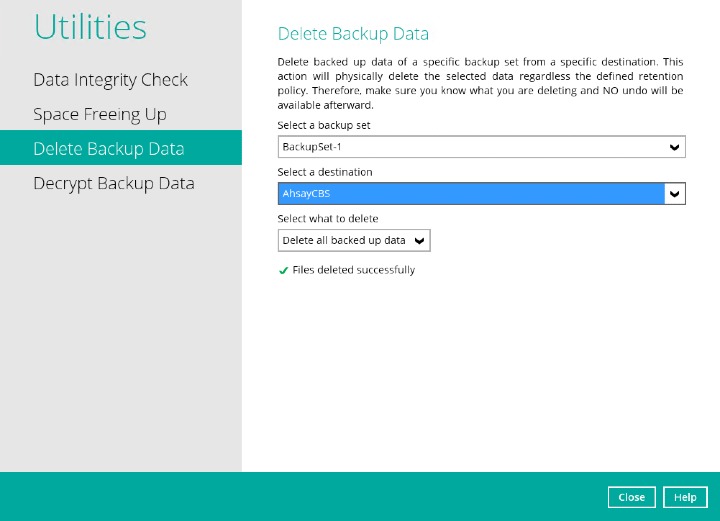
Delete Backup Data
This feature is used to permanently delete backed up data from a backup set(s), destination(s), backup job, or delete all backed up data. After the data is deleted, the storage statistics of the backup set(s) are updated.
Select a backup set from the drop-down list.
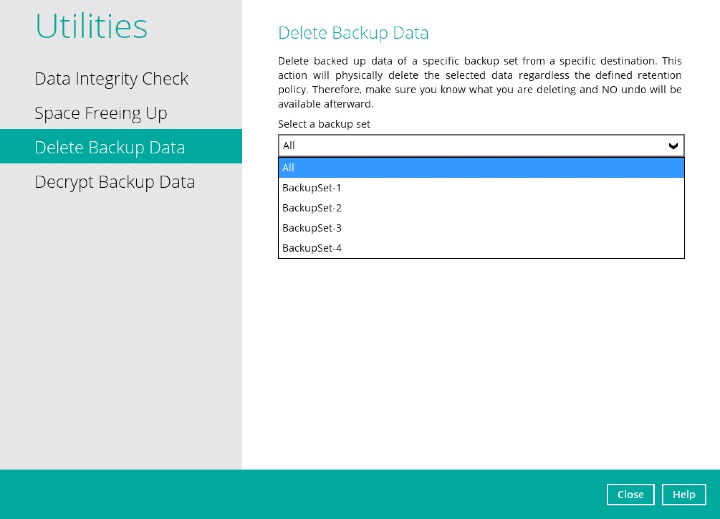
This will only delete the backed up files in a backup set(s) and destination(s), but the backup set and destination will remain.
Delete backup data action is not reversible. It will physically delete the selected backup data regardless of the defined retention policy settings. Therefore, make sure to select the correct backup data to be deleted before you proceed
If you select All backup sets, then there is no need to select a destination.
If you select a specific backup set, then you will also have to select a specific destination or all destinations.
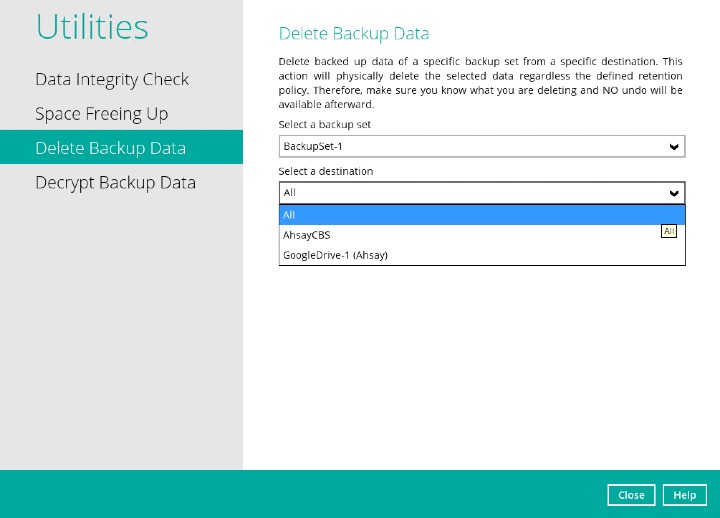
If you select a specific destination, there are two (2) available optoins for the type of files you wish to delete
- Delete all backed up data
- Choose from ALL files
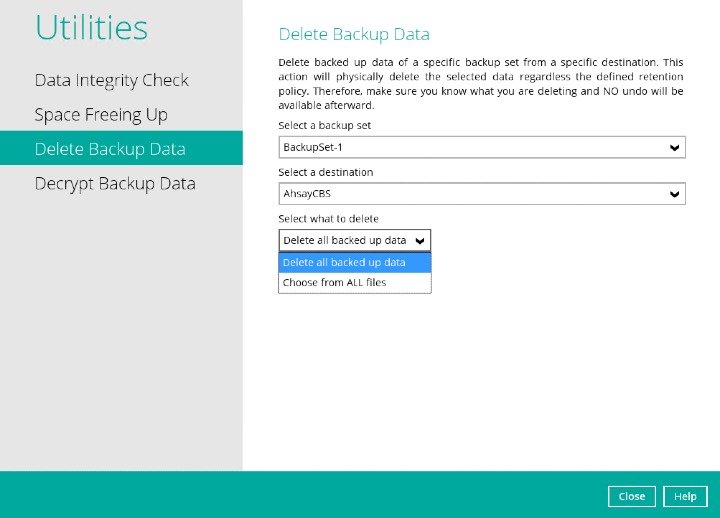
DELETE ALL BACKED UP DATA
If you choose this option, all backed up data from the selected backup set(s) and destination(s) will be deleted.
CHOOSE FROM ALL FILES
If you choose this option, you can select to delete any file(s) in the backup set
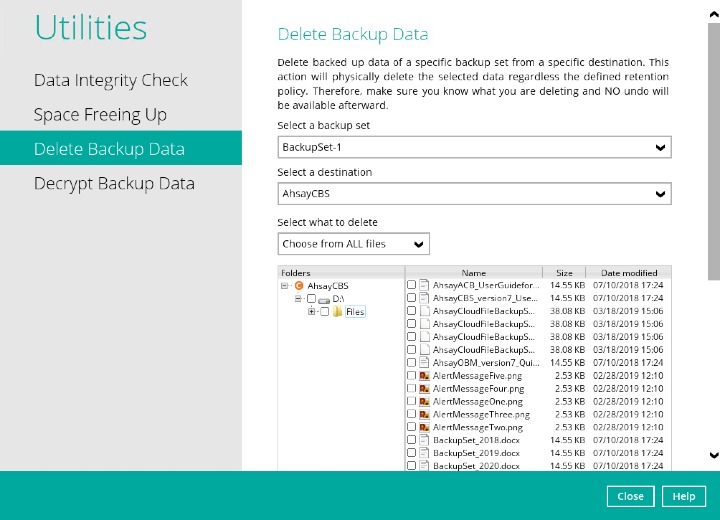
You also have the option to click the Search link to do an advanced search.
Click the Delete button.
Provide the passcode for 2FA

If the backup destination is immutable, space freeing up will not be allowed and this message will be displayed:
However, if deletion is enabled temporarily for the immutable backup destination, space freeing up will run after the passcode for 2FA is provided.
- The backup user account must be setup with 2FA in order to perform space free up from immutable backup destination.
- The passcode will only be required if 2FA is enabled for the user whether the backup destination is immutable or not. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
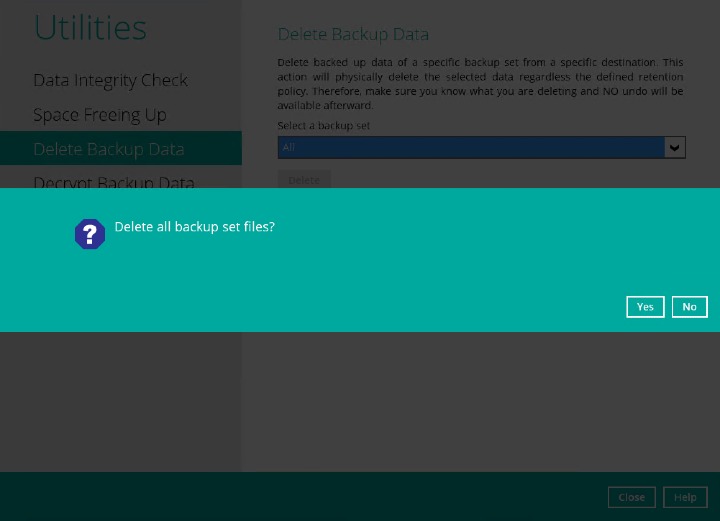
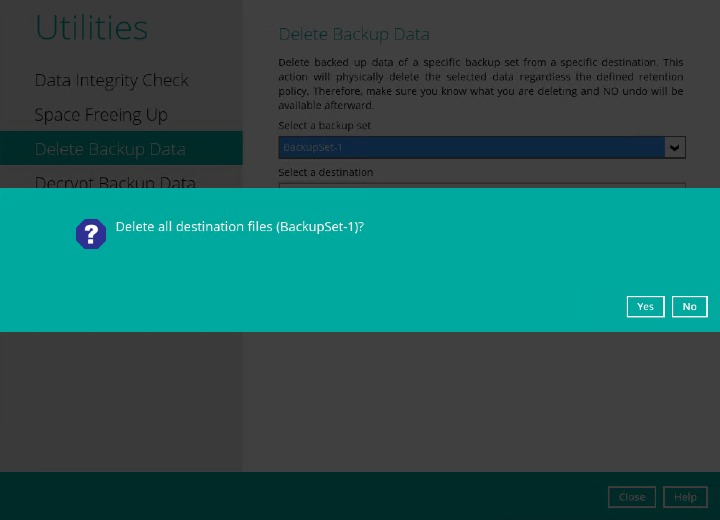
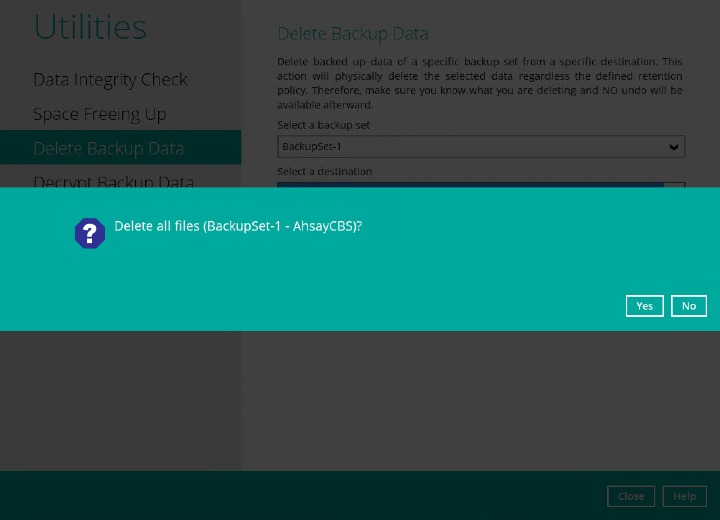
- Click the Yes to start the deletion of files. Here are examples of the confirmation message:
Delete all backed up data of all backup sets
Delete backed up data from all destinations of a specific backup set.
Delete all backed up data from a specific destination of a specific backup set.
Files are successfully deleted.
Decrypt Backup Data
This feature is used to restore raw data by using the data encryption key that was set for the backup set.
It can be used in the following situations:
- If the backup user has an old archive copy of their entire backup set on an external hard drive.
- A service provider is helping a customer recover data from the user’s AhsayCBS destination.
Perform Backup data Decryption
Click the Browse button to locate the path of the backup set ID/blocks folder.
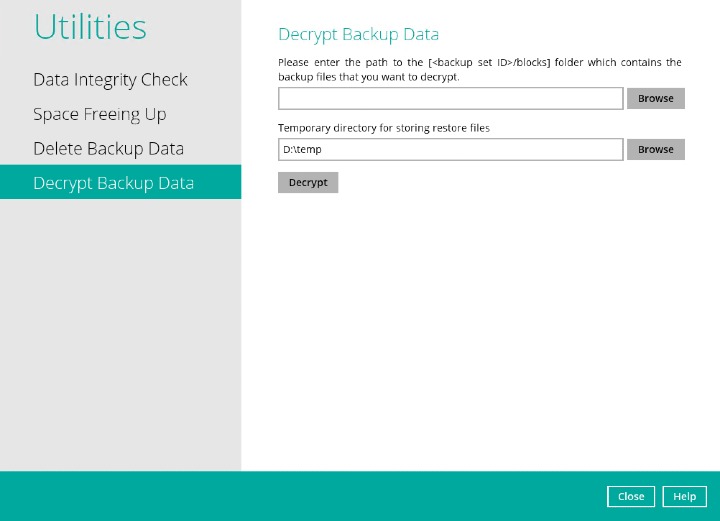
Click the Browse button to re-select the temporary folder for the decrypt process. Then click the Decrypt button to begin.
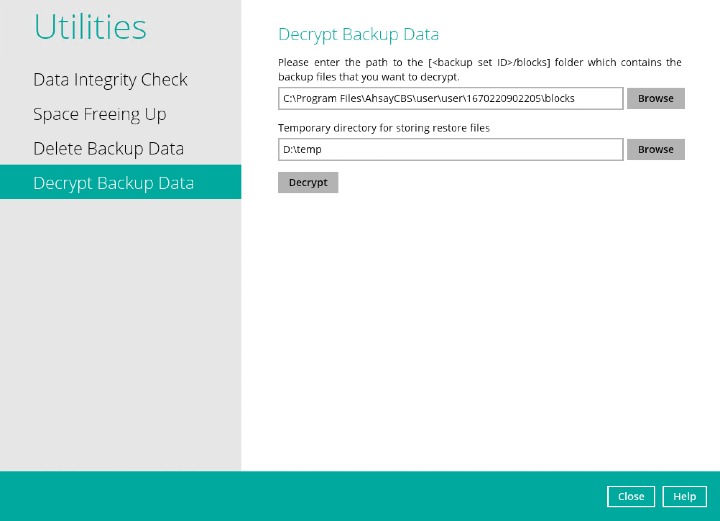 In the screenshot above, we are assuming that AhsayOBM is installed on the AhsayCBS server, and the “user” backup set path is “1670220902205”.
In the screenshot above, we are assuming that AhsayOBM is installed on the AhsayCBS server, and the “user” backup set path is “1670220902205”.Select files to be decrypted
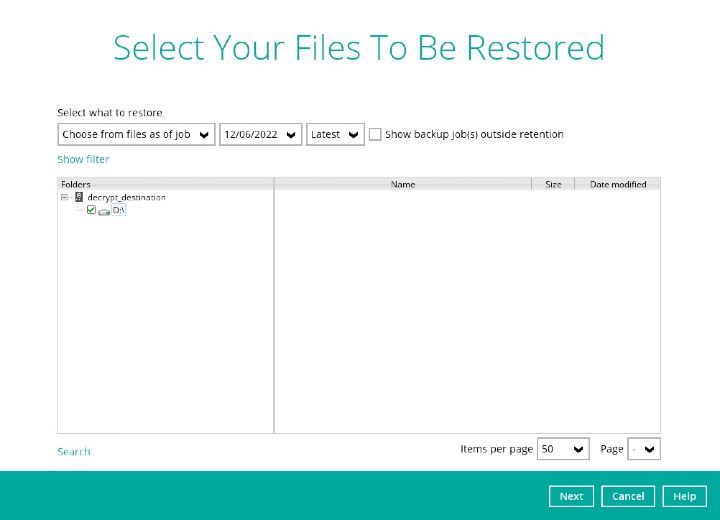
Choose the location where the decrypted files will be restored to then click Restore
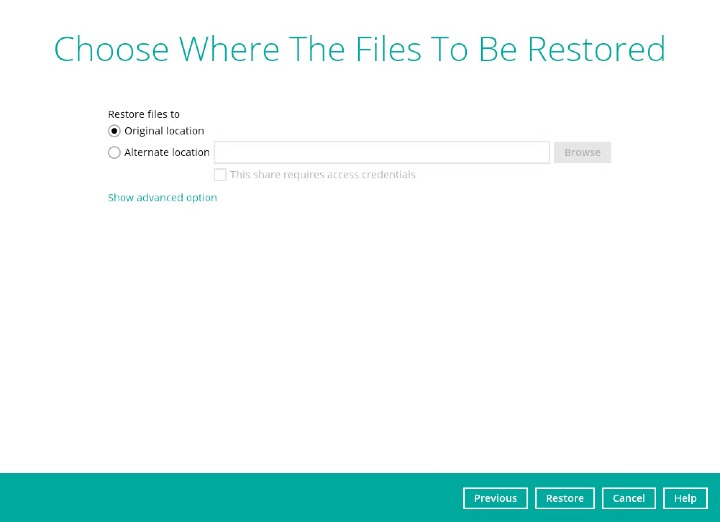
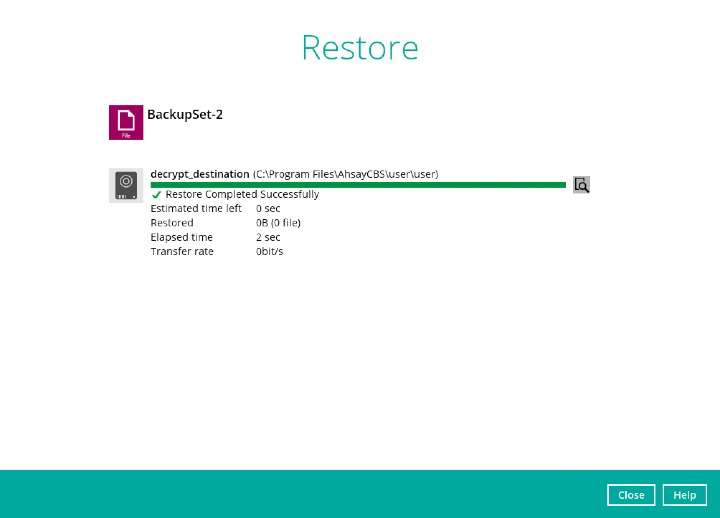
The status will be shown once completed.

 How-To
How-To