AhsayOBM MySQL Requirements
AhsayOBM Installation
Make sure that the latest version of AhsayOBM is installed on your computer with Internet access for connection to your MySQL Database Server.
For Linux, backup and restore of MS SQL Server database(s) running on a remote machine is not supported.
AhsayOBM Add-On Module Configuration
Make sure the MySQL Database Server module has been enabled in your AhsayOBM user account.
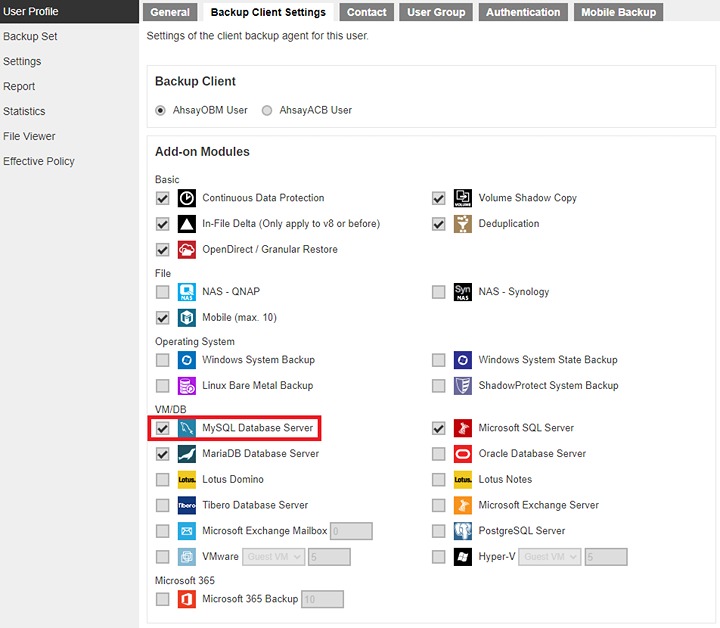
Please contact your backup service provider for more details.
Backup Quota Requirement
Make sure that your AhsayOBM user account has sufficient quota assigned to accomodate the storage of MySQL Database Server backup set and retention policy.
Please contact your backup service provider for more details.
Java Heap Size
The default Java heap size setting on AhsayOBM is 2048MB. It is highly recommended to increase the Java heap size setting to be at least 4096MB to improve backup and restore performance. The actual heap size is dependent on amount of free memory available on your MySQL Database Server.
Network Drive
The login accounts for network drives must have read and write access permission to ensure that backup and restore would be successful.
MySQL Database Server Requirements
Please ensure that the following requirements and conditions are met on the MySQL database server.
MySQL Version
AhsayOBM is installed on the MySQL database server for Windows and MySQL version 5.7 or above database server using the root account for Linux.
MySQL Database Status
The MySQL database instance is online.
Example: MySQL v5.6 on Windows Serer 2016 (64-bit), the default service name is MySQL56.
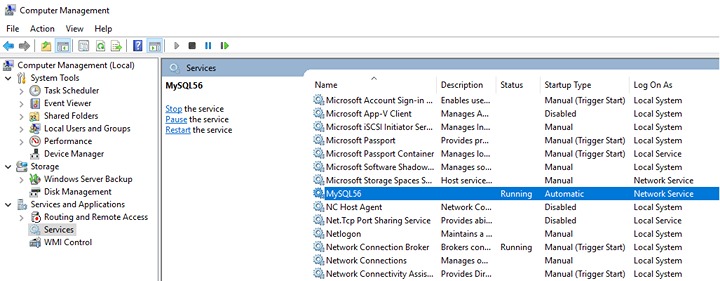
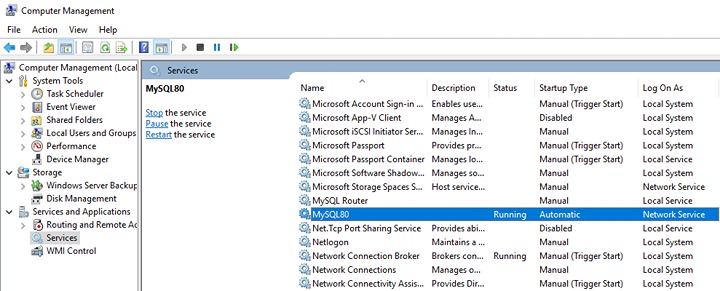
Example: MySQL v8 on Windows Server 2016, the default service name is MySQL80.
Example: MySQL 5.7 on CentOS 7
# service mysqld status
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status mysqld.service
- mysqld.service - MySQL Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service; enabled; vendor preset disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-02-04 11:42:08 HKT; 2h 46min ago
Docs: man:mysqld (8)
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html
Main PID: 16952 (mysqld)
CGroup: /system.slice/mysqld.service
16952 /usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-
file=/var/run/mysqld/my...
Jan 02 11:42:00 centos7 systemd[1]: Starting MySQL Server...
Jan 02 11:42:08 centos7 systemd[1]: Started MySQL Server.
TCP/IP Port
Check the listening port of the MySQL database instance (default is 3306).
Windows
C:\>netstat -b -a
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
RpcSs
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
Can not obtain ownership information
TCP 0.0.0.0:2179 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
[vmms.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:3306 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
[mysqld.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
TermService
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49665 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
[lsass.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49666 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
EventLog
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49667 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
[spoolsv.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49668 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
SessionEnv
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49669 w2k16-std:0 LISTENING
PolicyAgent
Linux
# netstat -an|more
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:60024 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 86 0 10.16.30.2:37272 203.186.85.237:443 CLOSE_WAIT
tcp 86 0 10.16.30.2:49302 40.114.13.14:443 CLOSE_WAIT
tcp 0 64 10.16.30.2:22 192.168.12.1:55777 ESTABLISHED
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 86 0 10.16.30.2:48396 10.16.30.21:443 CLOSE_WAIT
tcp6 86 0 10.16.30.2:48428 10.16.30.21:443 CLOSE_WAIT
MySQL Dump Utility
The mysqldump utility is installed on the MySQL database server.
Windows
Windows: the default location for the mysqldump utility for MySQL v5.6.x is located in the following folder:
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin
Linux
To locate the mysqldump utility use the "whereis" command.
# whereis mysqldump
mysqldump: /usr/bin/mysqldump /usr/share/man/man1/mysqldump.1.gz
MySQLDump Utility Version
The mysqldump utility is the same version as the MySQL database.
To check the mysqldump version use the mysqldump --version command.
Windows
Example: MySQL v5.6
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin>mysqldump --version mysqldump Ver 10.13 Distrib 5.6.41, for Win64 (x86_64)
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin>
Example: MySQL v8.0
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin>mysqldump --version mysqldump Ver 8.0.12 for Win64 on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin>
MySQL database version:
Example: MySQL v5.6
mysql> select version();
+------------+
| version() |
+------------+
| 5.6.41-log |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: MySQL v8.0
mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 8.0.12 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Linux
Example: MySQL 5.7 and CentOS 7.3
#mysqldump --version
mysqldump Ver 10.13 Distrib 5.7.23, for Linux (x86_64)
To check the MySQL database version either:
From the Linux command line, use the /usr/bin/mysql --version command.
# /usr/bin/mysql --version
/usr/bin/mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.23, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
Or
Log in to MySQL instance and use select version() ; command.
# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.23 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select version() ;
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 5.7.23 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: MySQL 8 on CentOS 7.4
To check the mysqldump version use the mysqldump --version command
# mysqldump --version
mysqldump Ver 8.0.11 for Linux on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
To check the MySQL database version either:
From the Linux command line use the /usr/bin/mysql --version command
# /usr/bin/mysql --version
/usr/bin/mysql Ver 8.0.11 for Linux x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
Or
Log in to MySQL instance and use the select version() ; command
# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 8.0.11 MySQL Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select version() ;
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 8.0.11 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
User Account Privileges
A MySQL database user account with the following privileges must be setup for the backup operation.
Example: MySQL v5.6
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO "username"@"localhost" IDENTIFIED BY "password";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO "username"@"localhost.localdomain" IDENTIFIED BY "password";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql>
For MySQL 8 the use of GRANT to define account authentication characteristic is deprecated. For more information, please refer to the MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual. As an alternative, you must first create the user and set the authentication characteristic by using CREATE USER before setting the privileges of the user using GRANT.
Example: MySQL v8.0
mysql> CREATE USER 'root'@'localhost.localdomain' IDENTIFIED BY 'Abcd123$%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.32 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost.localdomain';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
LocalHost
Verify that “localhost” on the MySQL database server is resolvable and “localhost” is allowed to access the MySQL database instance on the MySQL service listening port (default 3306).
C:\>ping localhost
Pinging 10.90.10.40 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.90.10.40: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 10.90.10.40: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 10.90.10.40: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 10.90.10.40: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 10.90.10.40:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
C:\>
# telnet localhost 3306
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost
Escape character is '^]'
J
5.6.31vB#'8%/kQ3K\n6' 'Aemysql_native_password
The telnet utility is not installed by default on some windows version.
MySQL Virtual System Databases
Exclude the “information_schema” and “performance_schema” databases which are MySQL virtual system databases, they contain information about the user databases on the MySQL instance. They are read-only and cannot be backed up.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sakila |
| test |
| world |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Temporary Directory
The databases selected for backup will be temporarily spooled to a temporary directory before being uploaded to the backup server or destination storage.
Ensure that the temporary directory configured for the MySQL database backup has sufficient disk space for the backup operation, the free space on the temporary directory drive should be at least 150% of the database size. As the temporary directory is also used for storing index files and any incremental or differential delta files generated during the backup job before they are uploaded to the backup destination.
Please bear in mind the size of the databases may grow over time and you may need to review the temporary directory free space requirements on a regular basis.
To calculate for the size of your databases run the command below.
mysql> SELECT table_schema AS "Database", ROUND(SUM(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS "Size (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY table_schema;
+--------------------+-----------+
| Database | Size (MB) |
+--------------------+-----------+
| information_schema | 0.01 |
| mysql | 0.90 |
| performance_schema | 0.00 |
| sakila | 6.44 |
| world | 0.77 |
+--------------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.53 sec)
mysql>

 How-To
How-To