Best Practices and Recommendations
The following are some best practices or recommendations that we strongly recommend, before you start any Microsoft System State backup and restore:
Temporary Directory Folder Location
For best performance, it is recommended that the temporary storage location of a MS Windows System State backup set is set to a supported local volume, and not to a network volume (e.g. to improve I/O performance). The temporary storage location is highly recommended to be set on a directory with sufficient free disk space and located to another location other than Drive C: (e.g. Drive D:).
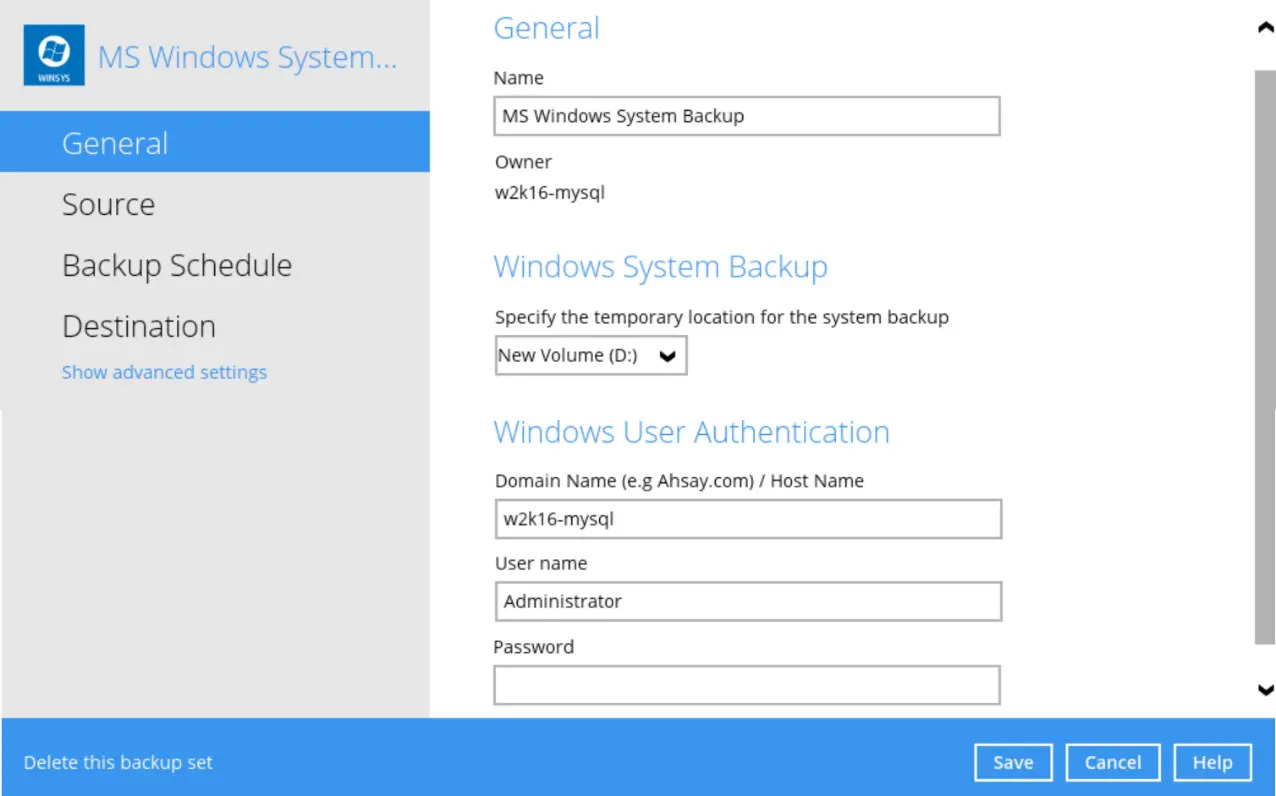
For Windows Server 2008 or newer releases, the restriction on temporary volume (found in the Requirements section) must also be considered.
Backup Destination
To provide maximum data protection and flexible restore options, it is recommended to configure:
- At least one offsite or cloud destination
- At least one local destination for fast recovery
Backup Frequency
MS Windows System State backup should be performed at least once per week.
Performance Recommendations
Consider the following best practices for optimized performance of the backup operations:
- Enable scheduled backup jobs when system activity is low to achieve the best possible performance.
- Perform test restores periodically to ensure your backup is set up and performed properly. Performing recovery test can also help identify potential issues or gaps in your recovery plan. It's important that you do not try to make the test easier, as the objective of a successful test is not to demonstrate that everything is flawless. There might be flaws identified in the plan throughout the test and it is important to identify those flaws.
It is highly recommended to enable the Include all critical volumes option to select all critical volumes for backup automatically.
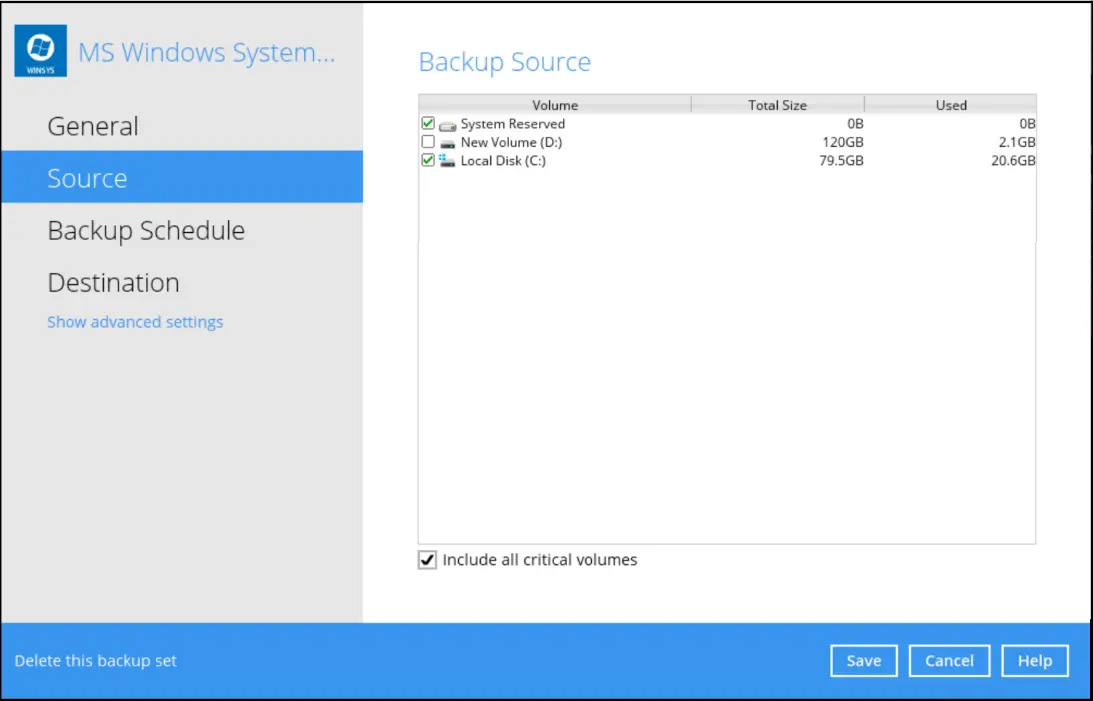
This will ensure that the backup image can be used for full-system / bare-metal recovery.
Not a Replacement for File Backup
An image-based / bare-metal backup should never be considered a replacement for a nightly data backup plan.
Firstly, image-based backups do not lend themselves easily to recovery of a single file. The nature of image-based backup requires a complete restore of the system image file, even if you only want to recover a single file.
Restore to Alternate Computer
You can restore a system state backup to the same physical computer from which the system state backup was created, or to a different computer that has the same make, model, and configuration (identical hardware). Microsoft does not support restoring a system state backup from one computer to a second computer of a different make, model, or hardware configuration.
Please refer to the following article for more details:
How to restore a Windows 7 installation
Periodic Backup Schedule
The periodic backup schedule should be reviewed regularly to ensure that the interval is sufficient to handle the data volume on the machine. Over time, data usage pattern may change on a production server, i.e. the number of new files created, the number of files which are updated/deleted, and new users may be added etc.
Consider the following key points to efficiently handle backup sets with periodic backup schedule.
- Hardware - to achieve optimal performance, compatible hardware requirements is a must. Ensure you have the backup machine’s appropriate hardware specifications to accommodate frequency of backups
- so that the data is always backed up within the periodic backup interval
- so that the backup frequency does not affect the performance of the production server
- Network - make sure to have enough network bandwidth to accommodate the volume of data within the backup interval.
- Retention Policy - also make sure to consider the retention policy settings and retention area storage management which can grow because of the changes in the backup data for each backup job

 Backup and Restore
Backup and Restore