Windows/Linux (GUI) Restore
The screenshots used for this guide are based on using AhsayOBM on Windows and will include screenshots for Linux (GUI) if applicable.
There are three (3) restore options to choose from:
- Original location - AhsayOBM will restore the database(s) from the backup destination and apply them to the original production Oracle instance.
- Alternate location - AhsayOBM will restore the database(s) from the backup destination and apply them to either the original Oracle instance or another Oracle instance on the production machine. This option can also be used to clone a database by changing the database name.
- Restore raw file - AhsayOBM will restore the Oracle database files to a location on the local machine, which then can be copied to another Oracle server on another machine for recovery.
The Restore Raw File option is for advanced Oracle database administrators and should only be used if you have in-depth knowledge and understanding of the Oracle database engine, Oracle database schema, knowledge of the database server, and network infrastructure. Therefore, it is not recommended to use this restore option as there is a need to utilize additional Oracle techniques and scripts to facilitate a manual database restore.
Please refer to the following articles of the Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for details:
Oracle 19c
Oracle 18c
Before restoring your Oracle database, check the following:
TNS listener service must be started to allow connections to the Oracle database server for the restore process. To check if the TNS listener service is running, use the lsnrctl status command. If the TNS listener service is not started, use the lsnrctl start command to start the service.
Example: A running TNS Listener service on Oracle 19c.
C:\Users\Administrator>lsnrctl status LSNRCTL for 64-bit Windows: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on 13-JUN-2023 15:46:48 Copyright (c) 1991, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connecting to (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=)(PORT=1521)) STATUS of the LISTENER ------------------------ Alias LISTENER Version TNSLSNR for 64-bit Windows: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Start Date 13-JUN-2023 15:38:22 Uptime 0 days 0 hr. 8 min. 26 sec Trace Level off Security ON: Local OS Authentication SNMP OFF Listener Parameter File D:\temp\WINDOWS.X64_193000_db_home\network\admin\listener.ora Listener Log File D:\oracle\diag\tnslsnr\ora19c-w2k16\listener\alert\log.xml Listening Endpoints Summary... (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=ora19c-w2k16)(PORT=1521))) (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(PIPENAME=\\.\pipe\EXTPROC1521ipc))) Services Summary... Service "1986bdcc8856453295755742c892092e" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl6", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "52448234712340b69f274bcc790ecfe0" has 2 instance(s). Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Instance "orcl6", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "9ea16c1ff5f944578d63d9d68979a5f9" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "CLRExtProc" has 1 instance(s). Instance "CLRExtProc", status UNKNOWN, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orcl" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orcl6" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl6", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orcl6XDB" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl6", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orcl6pd" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl6", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orclXDB" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "plug_db" has 1 instance(s). Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... The command completed successfully C:\Users\Administrator>The values shown are just examples and might be different on your Oracle instance.
Run the sqlplus / as sysdba command to verify if the Oracle service is active.
The following is just an example after an Oracle instance failure due to corrupted data and/or configuration files. It might be different on your Oracle instance.
C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Tue Jun 13 15:50:17 2023 Version 19.3.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition 2 Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.3.0.0.0This step is only for restoring to an Alternate location. Create a folder that will be used as the Alternate location of the database instance that will be restored. For example: D:\ORCL6.
Assign the correct permission to the created folder. To assign, right-click on the folder then select Properties.
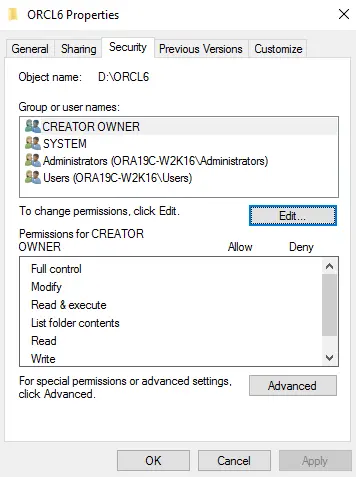
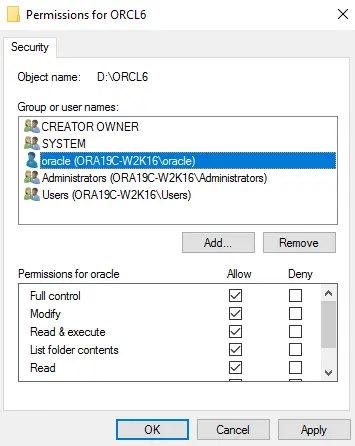
Go to the Security tab then click Edit.
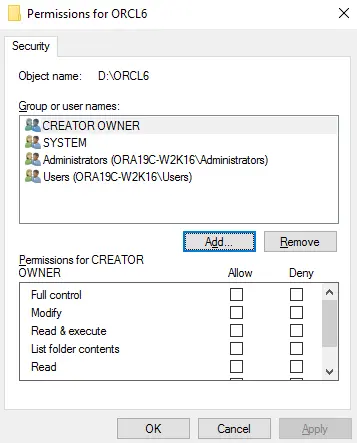
Click the Add button, then add the Oracle user account to the folder with Full control.
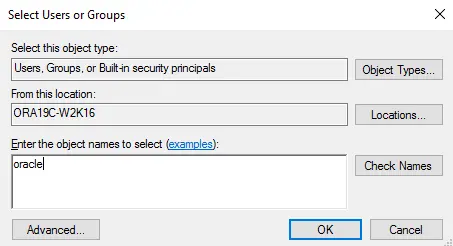
Click Apply, then click OK to save changes.
Please refer to the Troubleshooting - Example of Restore Log for Alternate location with Incorrect Permission Setup for more details.
Restore on Windows/Linux (GUI)
Click the Restore icon on the main interface of AhsayOBM.

Select the backup set and destination.
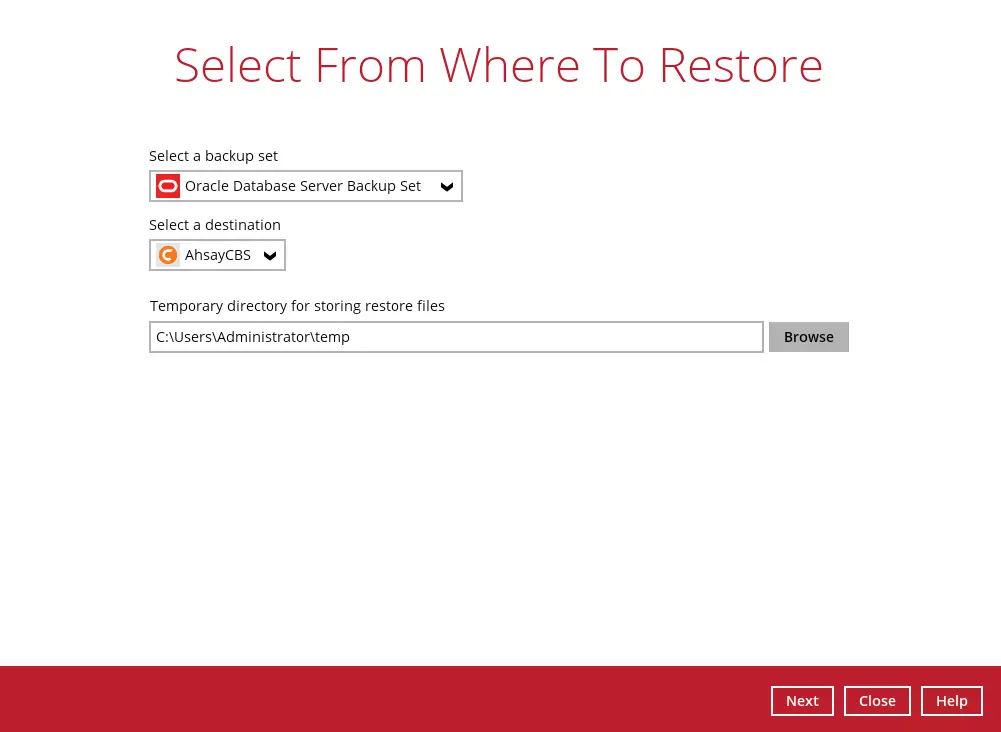
You can select the temporary directory for storing temporary files by clicking the Browse button.

This step will determine if the database will be restored automatically or manually.
For automatic restore, select the database(s) that you would like to restore. You can also choose to restore a backed-up database from a specific backup job using the “Select what to restore” drop-down menu.
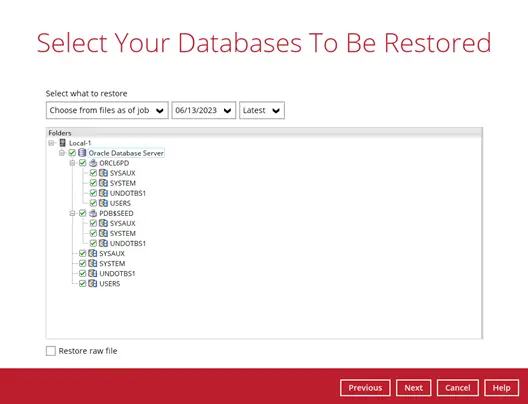
Or to manually restore the database, select the Oracle database(s) that you want to restore, then tick the Restore raw file option.
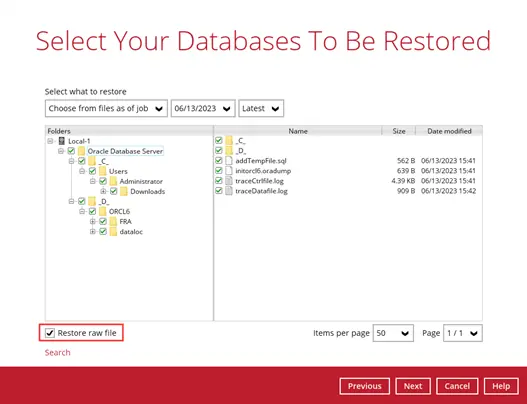
Click Next to proceed.
Select where to restore the database, either to the Original location or an Alternate location for automatic restore or select the path where you would like the raw file(s) to be restored for manual restore.

Restore to Original location

Restore to Alternate location

Configure the following settings in the Alternate database screen:
- Oracle Home - where the Oracle Home path is located. This is already set to the location of the Oracle Home by default.
- Host - this value is set to 127.0.0.1.
- Port - the new port number of the alternate Oracle database instance.
SID - the new SID for the alternate Oracle database instance.
If a restore will be performed to an alternate location, it is required to change the Oracle SID and port number.
- Password - the password for the system user account in the new database.
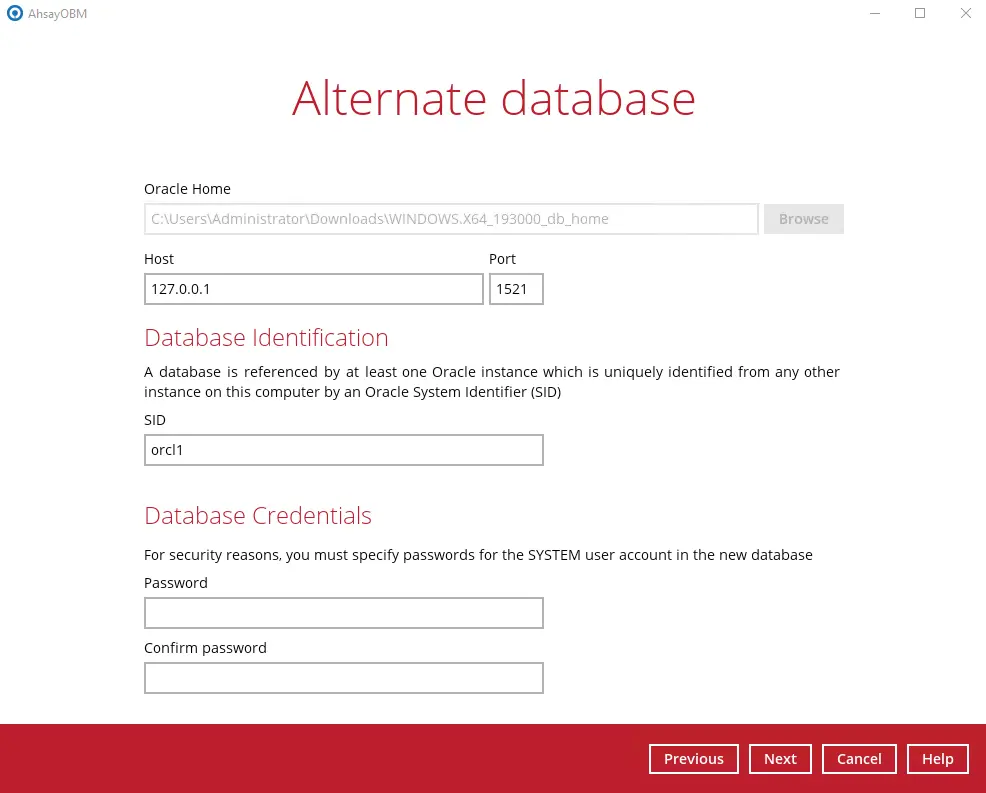
As the password validation is performed during the start of the actual restore process after the hostname, port number, SID, and all the database file locations are confirmed, ensure that you have entered the correct password in the Database Credentials.
Once configured, click Next to proceed.
Once the Oracle database instance has been modified, the changes will automatically be reflected in the original Database File Locations. Click Next to proceed.
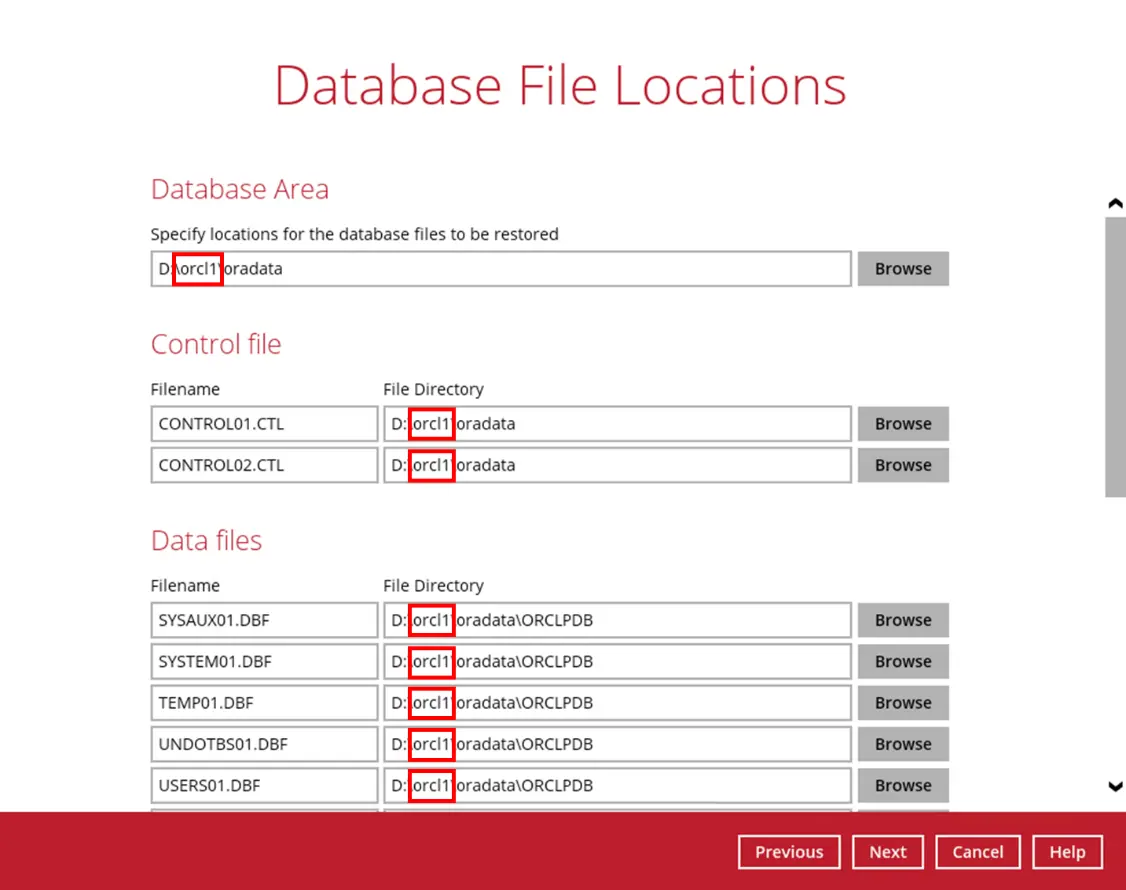
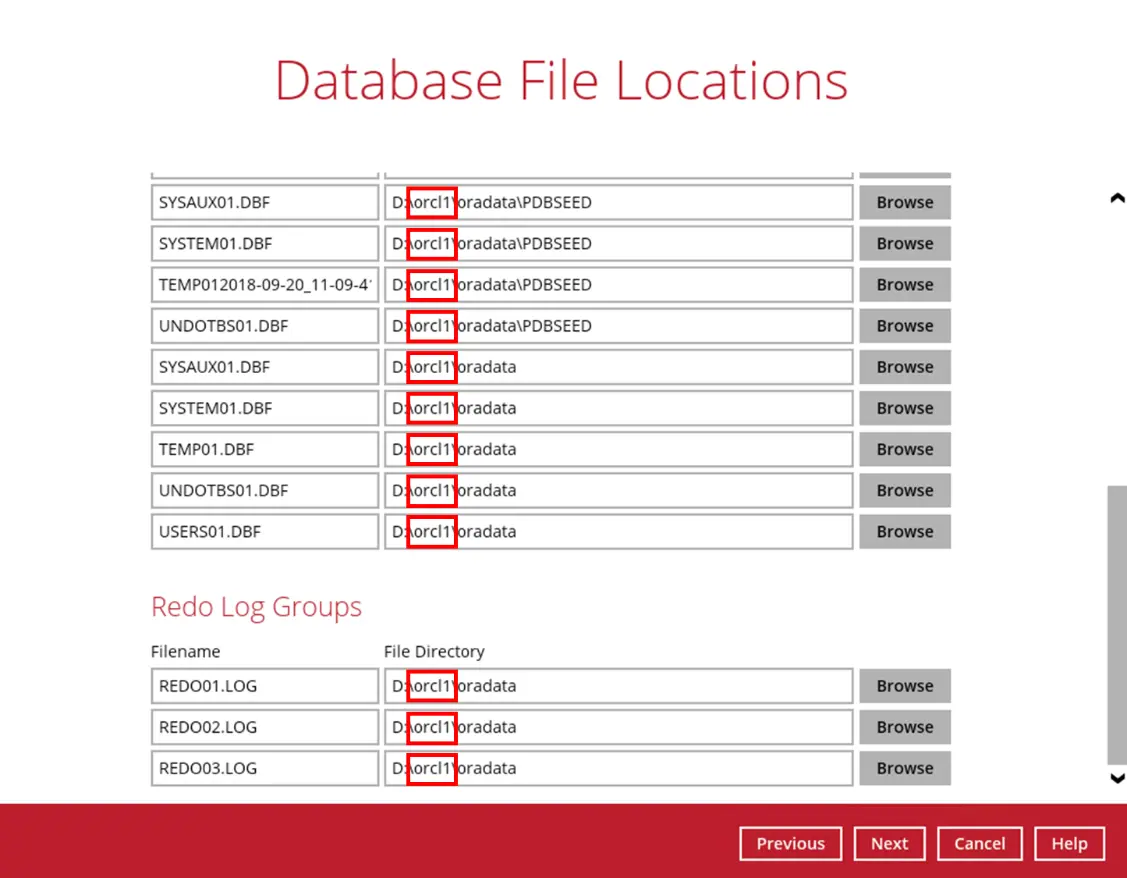
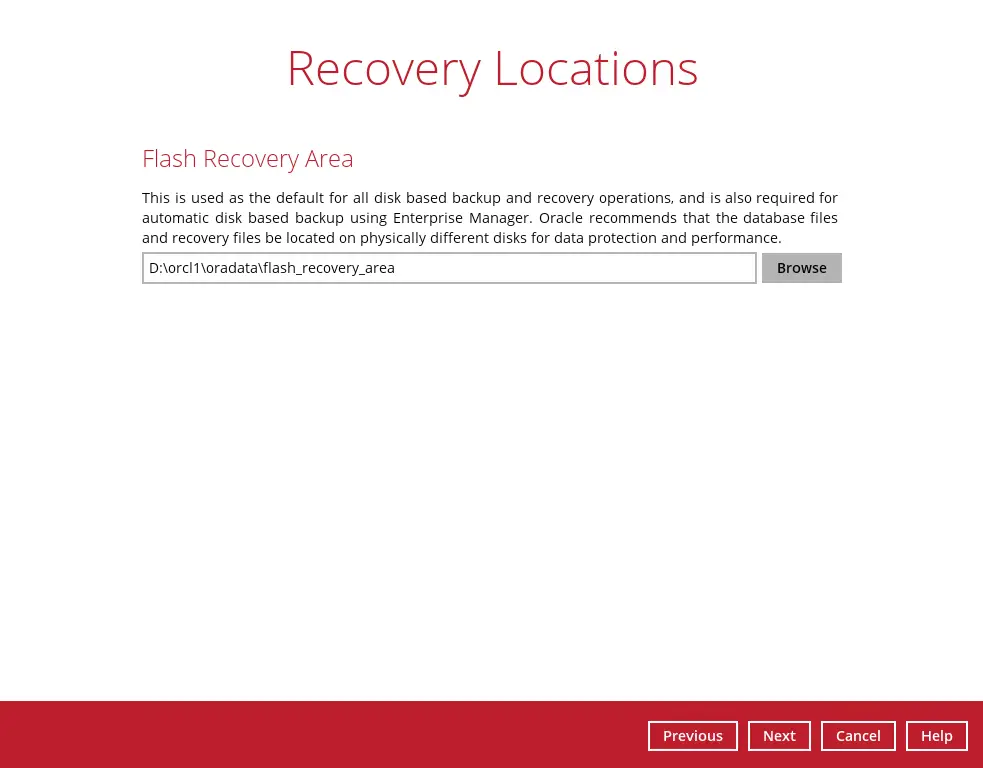
Select the path of the Recovery Location. Click Next to proceed.
Restore raw file
Click the Browse button to select the location on the local machine where you want to restore the Oracle database(s) to.
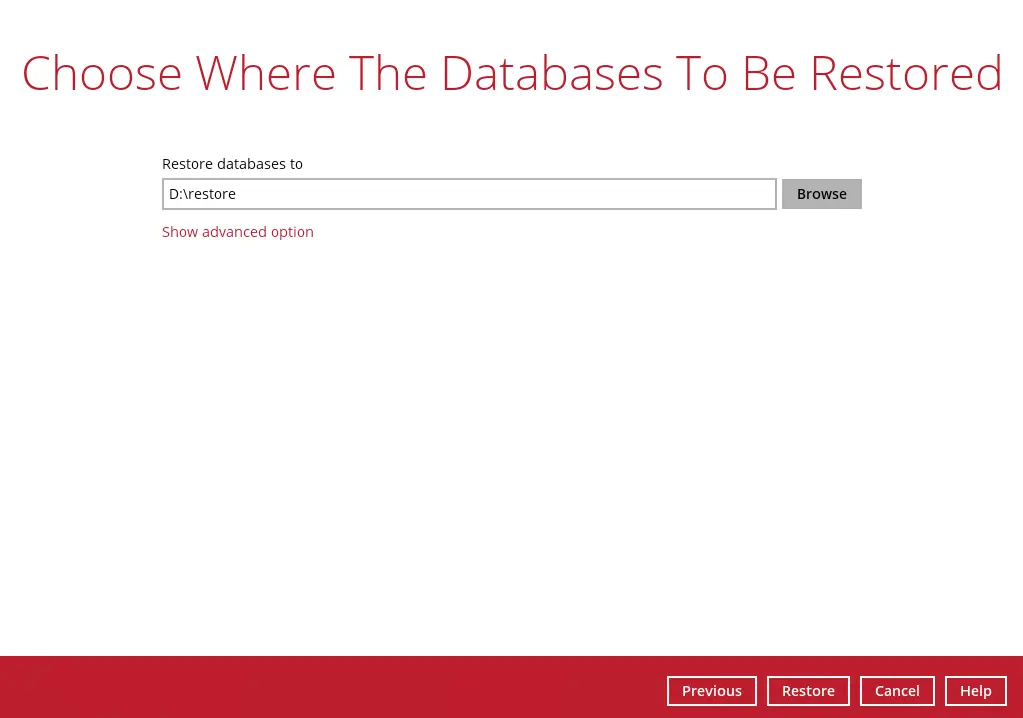
If you would like to enable the Verify checksum of in-file delta files during restore setting, click the Show advanced option link.

- Click Restore to start the restore process.
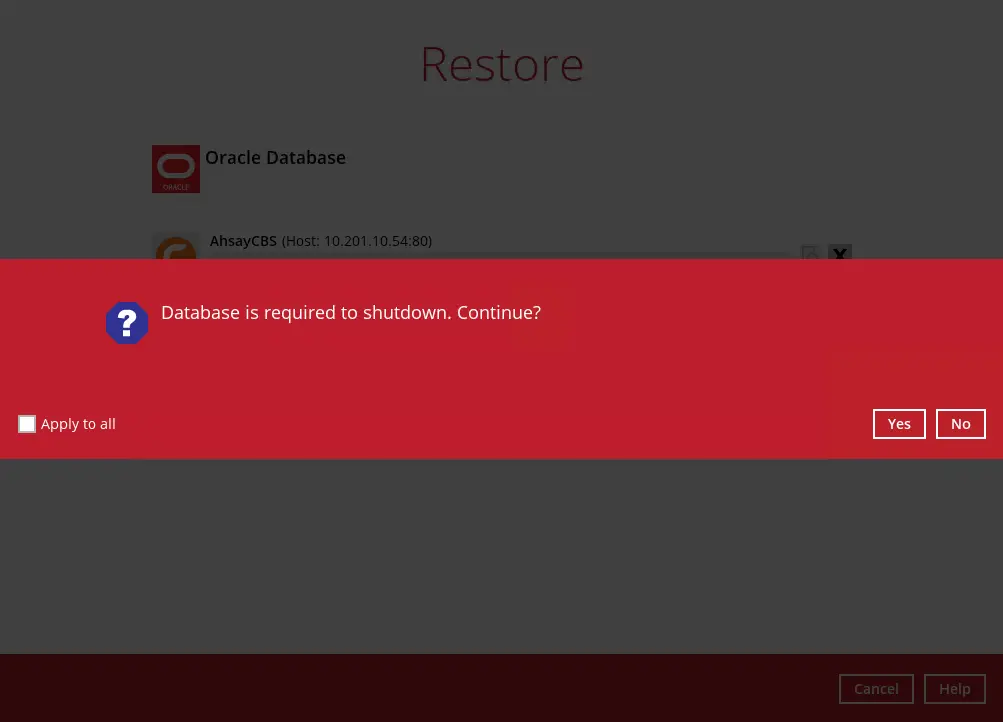
When this pop-up message is displayed, click Yes to continue.
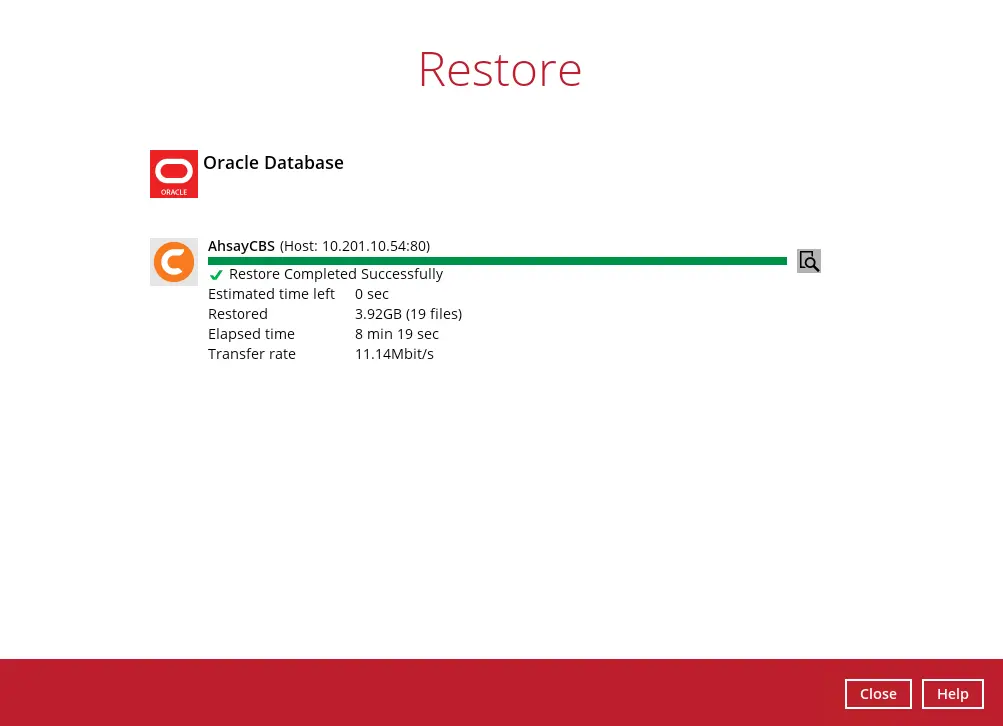
The restore job has completed successfully.
After the restore job is completed, you can verify if the Oracle database instance has been restored using the following SQL query to verify if the instance is online.
C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Wed Oct 14 14:07:32 2020 Version 19.3.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.3.0.0.0 SQL> select instance from v$thread; INSTANCE --------------------------------------------------------------- orcl SQL>
Only for Restore Raw File
After the restore job is completed, you can verify if the Oracle database(s) have been restored. Go to the designated path on the local machine where you restored the Oracle database files.
Example: Using Windows File Explorer
Recovering RAW Oracle databases
To recover RAW databases, please refer to the following articles of Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for details:
Oracle 19c
Oracle 18c
Oracle 12c

 Backup and Restore
Backup and Restore