Requirements
You are strongly recommended to configure or check all the settings below to confirm all the requirements are met before you proceed with the Oracle backup and restore.
AhsayOBM Installation
Make sure the latest version of AhsayOBM is installed directly on the machine where the Oracle database server is hosted.
Backup and restore of Oracle database(s) running on a remote machine is not supported.
AhsayOBM Add-On Module Configuration
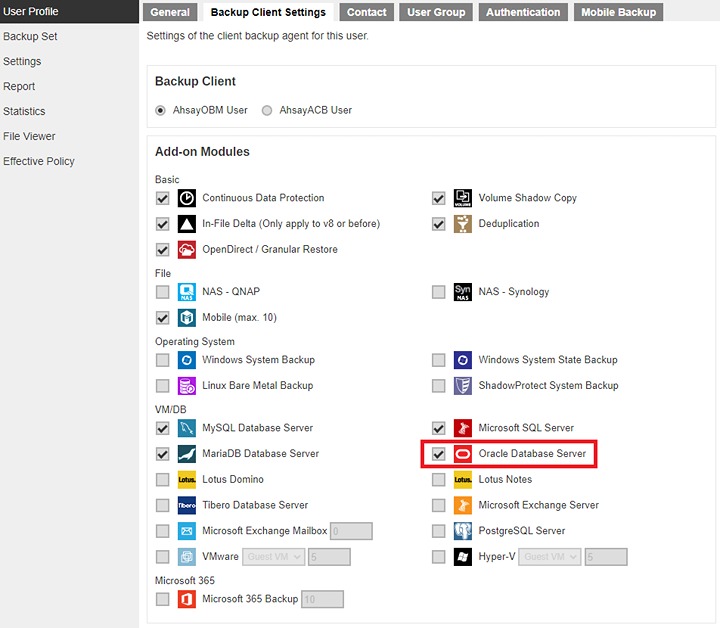
Make sure the Oracle Database Server add-on module is enabled on your AhsayOBM user account.
PLease contact your backup service provider for more details.
Backup Quota Requirement
Make sure that your AhsayOBM user account has enough storage quota assigned to accommodate the storage of the Oracle database server backup set and retention policy.
Java Heap Size
The default Java heap size setting on AhsayOBM is 2048MB. For Oracle database backup, it is highly recommended to increase the Java heap size setting to be at least 4096MB to improve backup and restore performance. The actual heap size is dependent on the amount of free memory available on your Oracle server.
For details on how to modify the Java heap size setting of AhsayOBM, refer to the following article:
How to modify the Java heap size setting of AhsayOBM / AhsayACB
Temporary Directory
The temporary directory folder is used by AhsayOBM during a backup job as the storage of spooled Oracle database(s) and archived log files.
It is strongly recommended that the temporary directory folder is located on a local drive with enough free disk space to be used by the spooled databases and archived log files. The temporary folder should not be located on the Windows System C:\ drive or Oracle Home drive.
The calculation of disk space required on the drive where the temporary folder is located is as follows: (Total Database Size * Delta Ratio) * number of backup destinations = Minimum Free Space Required.
Example:
If the default Delta ratio is 50% for in-file delta, and if the total Oracle database size is 1TB and there is only one backup destination, the minimum free space needed on the drive where the temporary directory folder is located = 1.5TB:
1TB = Total Oracle database size
500GB = Total maximum size of incremental or differential delta files generated
To obtain the size of the data files on the Oracle database instance, use the Oracle RMAN REPORT SCHEMA feature and sum up the total “List of Permanent Datafiles” by running the following command.
The values shown are just examples and might be different on your Oracle instance.
C:\Users\Administrator>set ORACLE_SID=orcl
C:\Users\Administrator>rman target /
Recovery Manager: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Thu Oct 29 18:29:44 2020
Version 19.3.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
connected to target database: ORCL (DBID=1562659286)
RMAN> report schema;
using target database control file instead of recovery catalog
Report of database schema for database with db_unique_name ORCL
List of Permanent Datafiles
===========================
File Size(MB) Tablespace RB segs Datafile Name
---- ------- ----------- -------- ----------------
1 910 SYSTEM YES D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\SYSTEM01.DBF
3 920 SYSAUX NO D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\SYSAUX01.DBF
4 60 UNDOTBS1 YES D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\UNDOTBS01.DBF
5 260 PDB$SEED:SYSTEM NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\PDBSEED\SYSTEM01.DBF
6 280 PDB$SEED:SYSAUX NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\PDBSEED\SYSAUX01.DBF
7 5 USERS NO D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\USERS01.DBF
8 100 PDB$SEED:UNDOTBS1 NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\PDBSEED\UNDOTBS01.DBF
9 260 ORCLPDB:SYSTEM NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\ORCLPDB\SYSTEM01.DBF
10 300 ORCLPDB:SYSAUX NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\ORCLPDB\SYSAUX01.DBF
11 100 ORCLPDB:UNDOTBS1 NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\ORCLPDB\UNDOTBS01.DBF
12 5 ORCLPDB:USERS NO
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\ORCLPDB\USERS01.DBF
List of Temporary Files
=======================
File Size(MB) Tablespace Maxsize(MB) Tempfile Name
---- -------- ----------- ----------- --------------------
1 32 TEMP 32767 D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\TEMP01.DBF
2 36 PDB$SEED:TEMP 32767
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\PDBSEED\TEMP012020-03-12_18-17-27-260-PM.DBF
3 128 ORCLPDB:TEMP 32767
D:\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORCL\ORCLPDB\TEMP01.DBF
RMAN>
Windows Requirements
Ensure that the following Windows requirements and conditions are met.
Supported WIndows Server Version
The backup of Oracle 19c is supported on the following Windows Server version:
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
User Account Permission
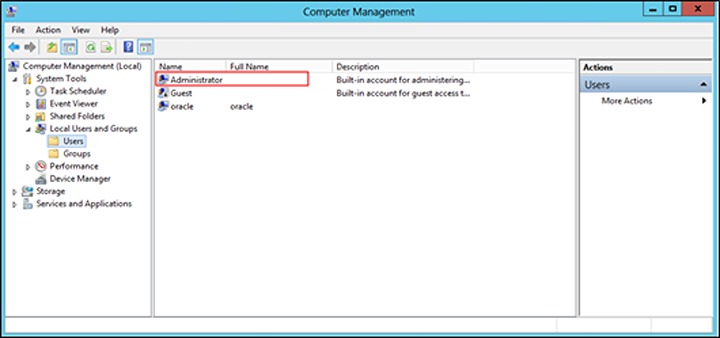
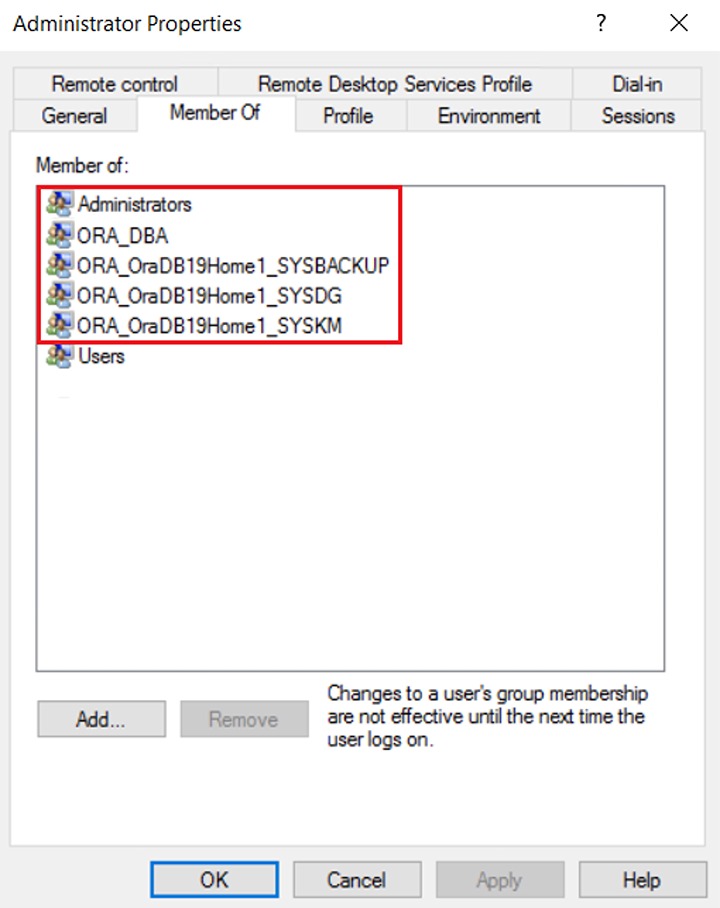
The Windows user account must be a member of the following security groups:
- Administrator
- ORA_DBA
- ORA_OraDB19Home1_SYSBACKUP
- ORA_OraDB19Home1_SYSDG
- ORA_OraDB19Home1_SYSKM
To verify, click the start menu and search for “Computer Management”. Open the application. Locate the Oracle security groups through Computer Management (Local) > System Tools > Locals Users and Groups > Users. Right-click the Administrator and select Properties.
Click the Member Of tab to see the list of Oracle security groups.
Oracle Database-Related Windows Services
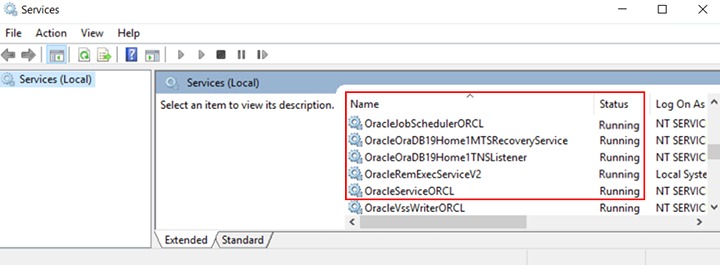
Ensure that all Oracle database-related services are started:
- OracleJobScheduler$SID$
- OracleOraDB19Home1MTSRecoveryService
- OracleOraDB19Home1TNSListener
- OracleRemExecServiceV2
- OracleService$SID$
To verify, click the start menu and search for “Services”. Look for the Oracle database-related services. Their statuses should be “Running”.
Linux Requirements
Ensure that the following Linux requirements and conditions are met.
Supported OS Version
Oracle 19c
The backup of Oracle 19c is supported on the following OS versions:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 and 8 (or above)
Oracle 18c
The backup of Oracle 18c is supported on the following OS versions:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.4 and 7 (or above)
GUI Desktop Environment
The Linux machine must be installed with a GUI desktop environment (i.e., GNOME, KDE, Cinnamon, etc.).
Oracle Backup Requirements
Ensure that the following requirements and conditions on the Oracle database server are met.
Please consult your Oracle database administrator before making any changes.
Oracle Backup Requirements
Ensure that the following requirements and conditions on the Oracle database server are met.
Please consult your Oracle database administrator before making any changes.
Oracle Tools
Although the following tools are usually installed by default on all Oracle database installations, ensure that the following tools are installed on the Oracle database server, and functioning correctly
RMAN (Recovery manager) - is require by AhsayOBM for both full database and archive log backups.
To verify if RMAN is installed on the Oracle database server and is working properly, run the following command.
EXAMPLE OF RMAN RUNNING IN ORACLE 19C
C:\Users\Administrator<set ORACLE_SID=orcl C:\Users\Administrator<rman target / Recovery Manager: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Mon Feb 7 09:36:48 2022 Version 19.3.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. connected to target database: ORCL (DBID=1562659286) RMAN>SQL*Plus - is required by AhsayOBM during Oracle Backup Set creation, backup and restore.
To verify if SQL*Plus is installed on the Oracle database server and is working properly, run the following command sqlplus / as sysdba.
EXAMPLE OF SQL*PLUS RUNNING IN ORACLE 19C
C:\Users\Administrator<sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Mon Feb 7 09:41:15 2022 Version 19.3.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.3.0.0.0 SQL>
Oracle Internal Process Checking
For the Oracle instance to run smoothly, ensure that the following internal processes are working well:
- PMON (Process Monitor)
- PSPO (Process Spawner Process)
- MMAN (Memory Manager Process)
- DBWO (Database Writer)
- ARCO (Archive Process (or thread on Windows))
- LGWR (Log Writer)
- CKPT (Checkpoint process (thread on Windows) that runs by default on Windows)
- SMON (System Monitor)
- RECO (Distributed Recovery Background Process)
To check this, click the start menu and search for “cmd”. Open the command prompt as administrator.
Run the SQLPlus to connect to the Oracle database server. Once connected, use the following SQL query to verify if the internal processes are running.
C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Wed Oct 14 14:07:32 2020
Version 19.3.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 19.3.0.0.0
SQL> select name, description from v$bgprocess where PADDR <> '00';
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
PMON process cleanup
CLMN process cleanup
PSP0 process spawner 0
VKTM Virtual Keeper of TiMe process
GEN0 generic0
MMAN Memory Manager
W007 space management slave pool
GEN1 generic1
DIAG diagnosibility process
DBRM DataBase Resource Manager
VKRM Virtual sKeduler for Resource Manager
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
SVCB services background monitor
PMAN process manager
DIA0 diagnosibility process 0
DBW0 db writer process 0
LGWR Redo etc.
CKPT checkpoint
SMON System Monitor Process
LG00 Log Writer Slave
SMCO Space Manager Process
LG01 Log Writer Slave
RECO distributed recovery
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
W000 space management slave pool
LREG Listener Registration
W001 space management slave pool
PXMN PX Monitor
FENC IOServer fence monitor
P000 Parallel query slave
MMON Manageability Monitor Process
MMNL Manageability Monitor Process 2
D000 Dispatchers
S000 Shared servers
TMON Transport Monitor
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
P001 Parallel query slave
M003 MMON slave class 1
P002 Parallel query slave
TT00 Redo Transport
ARC0 Archival Process 0
TT01 Redo Transport
ARC1 Archival Process 1
ARC2 Archival Process 2
ARC3 Archival Process 3
TT02 Redo Transport
W002 space management slave pool
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
W003 space management slave pool
AQPC AQ Process Coord
W004 space management slave pool
P003 Parallel query slave
P004 Parallel query slave
P005 Parallel query slave
P006 Parallel query slave
P007 Parallel query slave
M005 MMON slave class 1
QM02 QMON MS
W005 space management slave pool
NAME DESCRIPTION
----- --------------------------------------------------------
M001 MMON slave class 1
Q003 QMON MS
M000 MMON slave class 1
CJQ0 Job Queue Coordinator
M002 MMON slave class 1
W006 space management slave pool
Q00L QMON MS
62 rows selected.
SQL>
Supported Oracle Database Server Version
AhsayOBM supports the following versions of Oracle database server:
- Oracle 19c
- Oracle 18c
- Oracle 12c
To verify if the Oracle database server version is supported by AhsayOBM, use the following SQL query.
Example: Oracle 19c
C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Mon Feb 7 12:04:25 2022
Version 19.3.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 19.3.0.0.0
System Identifier (SID)
Make sure the System Identifier (SID) is correct by using the following SQL query.
Windows
SQL> select instance from v$thread; INSTANCE --------------------------------------------------------------- orcl SQL>Linux
SQL> select instance from v$thread; INSTANCE --------------------------------------------------------------- cdb1 SQL>
The instance shown is just an example. The SID may be different on your Oracle instance.
Another way to verify the SID is by checking the init.ora file. Go to the:
D:\oracle\admin\orcl\pfile - directory for Windows/u01/app/oracle/admin/cdb1/pfile - directory for Linux
Then, open the init.ora file using a text editor (e.g. Notepad++ for Windows and vi for Linux).
###########################################
# Database Identification
###########################################
db_name="orcl"
ORACLE_HOME PATH
Example: Oracle 19c
The Oracle_Home path can be obtained by using the following SQL query. The Oracle_Home path for Oracle 19c is “D:\app\oracle\19.0.0\dbhome_1” for Windows and “/u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1” for Linux.
SQL> SELECT file_spec FROM DBA_LIBRARIES WHERE library_name =
'DBMS_SUMADV_LIB';
FILE_SPEC
---------------------------------------------------------------
D:\app\oracle\19.0.0\dbhome_1\bin\oraqsmashr.dll
SQL>
The instance shown is just an example. The SID may be different on your Oracle instance.
Another way to verify the Oracle_Home path is by checking the init.ora file. Go to the D:\oracle\admin\orcl\pfile directory and open the init.ora file using a text editor (e.g. Notepad++ for Windows and vi for Linux).
###########################################
# File Configuration
###########################################
control_files=("D:\app\oracle\oradata\ORCL\control01.ctl",
"D:\app\oracle\oradata\ORCL\control02.ctl")
###########################################
Example of an SQL query return with a null value of the Oracle_Home path
If any of the following scenario is encountered, please contact the Oracle database administrator for further assistance:
- The value of the Oracle_Home path in init.ora file does not match the value obtained from the SQL query.
- The SQL query returns an empty or null value.
SQL> SELECT file_spec FROM DBA_LIBRARIES WHERE library_name =
'DBMS_SUMADV_LIB';
no rows selected
SQL>
DATABASE STATUS
Ensure that the status of Oracle isntance is "Open". To check, use the following query.
SQL> select instance_name, status from v$instance;
INSTANCE_NAME STATUS
-------------- ---------------------------------------------
orcl OPEN
SQL>
ARCHIVED LOG MODE
Ensure that the database instance is in Archived Log mode. To check, use the following command.
SQL> archive log list;
Database log mode Archive Mode
Automatic archival Enabled
Archive destination USE_DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST
Oldest online log sequence 101
Next log sequence to archive 103
Current log sequence 103
SQL>
The values shown are just examples and might be different on your Oracle instance.
JAVA INSTALLATION
Java must be installed on the Oracle Database. To check if Java is installed, use the following SQL query. The status of the JServer JAVA Virtual Machine and Oracle Database Java Packages should be “VALID”.
SQL> select comp_name, status from dba_registry;
COMP_NAME STATUS
-------------- ------------
Oracle Database Catalog Views VALID
Oracle Database Packages and Types VALID
Oracle Real Application Clusters OPTION OFF
COMP_NAME STATUS
-------------- ------------
JServer JAVA Virtual Machine VALID
Oracle XDK VALID
Oracle Database Java Packages VALID
COMP_NAME STATUS
-------------- ------------
OLAP Analytic Workspace VALID
Oracle XML Database VALID
Oracle Workspace Manager VALID
COMP_NAME STATUS
-------------- ------------
Oracle Text VALID
Oracle Multimedia VALID
Spatial VALID
COMP_NAME STATUS
-------------- ------------
Oracle OLAP API VALID
Oracle Label Security VALID
Oracle Database Vault VALID
15 rows selected.
SQL>
If the status of the JServer JAVA Virtual Machine and/or the Oracle Database Java Packages is INVALID, please contact the Oracle database administrator for further assistance.
JAVASYSPRIV PERMISSION FOR ORACLE SYSTEM ACCOUNT
The Oracle system account is used by AhsayOBM to connect to the Oracle database server to authenticate the backup and restore process. The following permission must be assigned to the system account. Use the following SQL query to assign.
SQL> select * from DBA_ROLE_PRIVS where upper(grantee)='SYSTEM';
GRANTEE GRANTED_ROLE ADM DEL DEF COM INH
------- ---------- --- --- --- --- ---
SYSTEM DBA NO YES NO
SYSTEM JAVASYSPRIV NO YES NO
GRANTEE GRANTED_ROLE ADM DEL DEF COM INH
------- ---------- --- --- --- --- ---
SYSTEM DBA NO YES NO
SYSTEM AQ_ADMINISTRATOR_ROLE YES NO YES NO
SQL>
If not, grant javasyspriv to the system account by using the following SQL query.
SQL> grant javasyspriv to system;
Grant succeeded.
SQL>
SYSDBA PRIVILEGES FOR ORACLE SYSTEM ACCOUNT
To check if the system account has sysdba privileges, use the following SQL query.
SQL> select * from v$pwfile_users where sysdba='TRUE';
USERNAME SYSDB SYSOP SYSAS SYSBA SYSDG SYSKM ACCOUNT_STATUS
-------- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- --------------
SYST TRUE FALSE FALSE OPEN
SQL>
If not, grant sysdba to the system account using the following SQL query.
Oracle 19c ad Oracle 18c
SQL> grant sysdba to system container=ALL; Grant succeeded. SQL>Oracle 12c
SQL> grant sysdba to system; Grant succeeded. SQL>
TNS LISTENER SERVICE
TNS listener service must be started to allow connections to the Oracle database server. To check if the TNS listener service is running, use the "lsnrctl status" command.
If the TNS listener service is not started, use the "lsnrctl start" command to start the service.
Example: A running TNS Listener service on Oracle 19c
C:\Users\Administrator>lsnrctl status
LSNRCTL for 64-bit Windows: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on 14-OCT2020 16:45:29
Copyright (c) 1991, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=ora19cw2k16)(PORT=1521)))
STATUS of the LISTENER
------------------------
Alias LISTENER
Version TNSLSNR for 64-bit Windows: Version 19.0.0.0.0
- Production
Start Date 07-FEB-2022 11:11:04
Uptime 0 days 5 hr. 34 min. 27 sec
Trace Level off
Security ON: Local OS Authentication
SNMP OFF
Listener Parameter File
D:\oracle\19.3.0\dbhome\network\admin\listener.ora
Listener Log File D:\oracle\diag\tnslsnr\ora19cw2k16\listener\alert\log.xml
Listening Endpoints Summary...
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=ora19c-w2k16)(PORT=1521)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(PIPENAME=\\.\pipe\EXTPROC1521ipc)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=ora19cw2k16)(PORT=5500))(Security=(my_wallet_directory=D:\ORACLE\admin\orcl\xdb
_wallet))(Presentation=HTTP)(Session=RAW))
Services Summary...
Service "52448234712340b69f274bcc790ecfe0" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "9400891b61bb4c4c8b3997957ffa8c8e" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "CLRExtProc" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "CLRExtProc", status UNKNOWN, has 1 handler(s) for this
service...
Service "orcl" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "orclXDB" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "orclpdb" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
The command completed successfully
C:\Users\Administrator>
The values shown are just examples and might be different on your Oracle instance.
LOCALHOST IS RESOLVABLE
Verify if the localhost IP 127.0.0.1 on the Oracle database server is resolvable using the command "ping 127.0.0.1" as this will be the IP address that AhsayOBM will use to connect to the Oracle instance.
C:\Users\Administrator>ping 127.0.0.1
Pinging 127.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 127.0.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 127.0.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 127.0.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 127.0.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 127.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
C:\Users\Administrator>
ORACLE PORT NUMBER
The default Oracle port number is 1521. To check, use the "netstat" and "tnsping" commands to verify the actual port number.
NETSTAT
C:\Users\Administrator>netstat -pan|more
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:1521 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:2179 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:5500 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:5985 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:47001 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49664 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49665 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49666 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49667 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49668 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49669 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49670 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:49697 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 10.16.10.123:139 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 10.16.10.123:2030 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
TCP 10.16.10.123:3389 192.168.12.1:56719 ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.16.10.123:49671 40.90.189.152:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.16.10.123:49690 40.90.189.152:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.16.10.123:51761 ti-in-f95:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 127.0.0.1:1521 ora19c-w2k16:51740 ESTABLISHED
TCP 127.0.0.1:51740 ora19c-w2k16:1521 ESTABLISHED
TCP 172.16.10.123:139 ora19c-w2k16:0 LISTENING
-- More --
The values shown are just examples and might be different on your Oracle instance.
TNSPING
C:\Users\Administrator>tnsping 127.0.0.1
TNS Ping Utility for 64-bit Windows: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on
14-OCT-2020 16:54:27
Copyright (c) 1997, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Used parameter files:
D:\oracle\19.3.0\dbhome\network\admin\sqlnet.ora
Used EZCONNECT adapter to resolve the alias
Attempting to contact
(DESCRIPTION=(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=
127.0.0.1)(PORT=1521)))
OK (10 msec)
C:\Users\Administrator>

 Backup and Restore
Backup and Restore